EasySend's Formula Editor
The Formula editor enables EasySend's platform users to use built-in operators, functions, and model data items to create simple and complex conditions, logical expressions, and calculations.
Where to Find the Formula Editor
(See Figure 1 and Figure 2)
After clicking a data item, the Formula editor can be found in two locations on the Model screen:
- Under the Values feature (1), when clicking the Value dropdown (2), the Formula (3) is the second option to select:
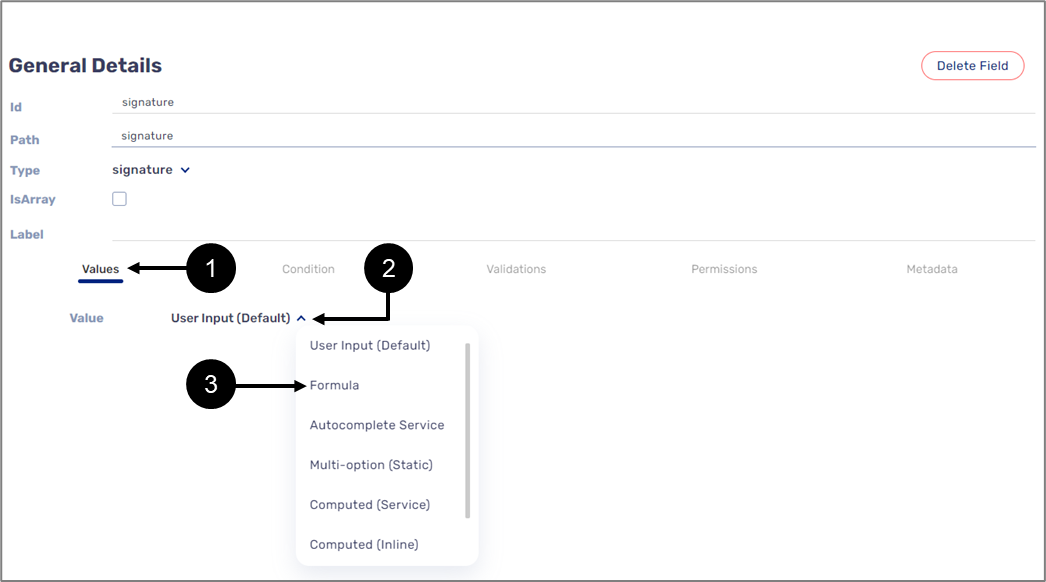
Figure 1: Formula Under Values
- Under the Condition feature (1), when clicking the dropdown (2) under Visibility or the Edit (Disable) conditions, the formula (3) is the second option to select:
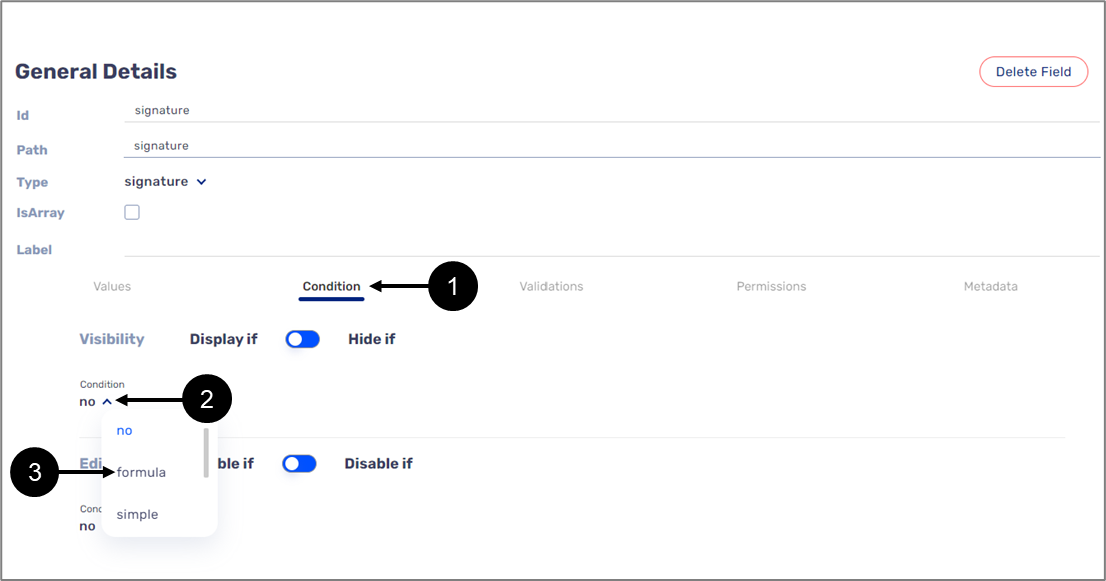
Figure 2: Formula Under Condition
Formula Editor Structure
(See Figure 3)
When selecting the Formula option (under Values or Condition), the formula display window (1) and the Edit Formula button (2) appear.
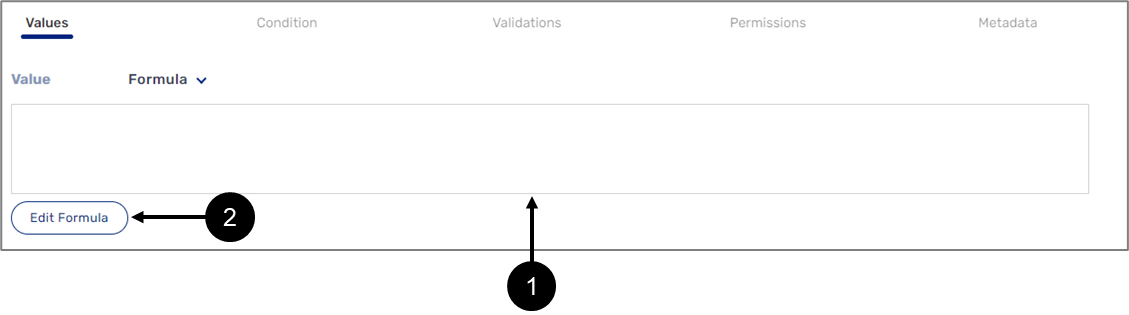
Figure 3: Formula
The Formula Editor Window
Figure 4 and Table 1 describe the structure of the Formula Editor window.
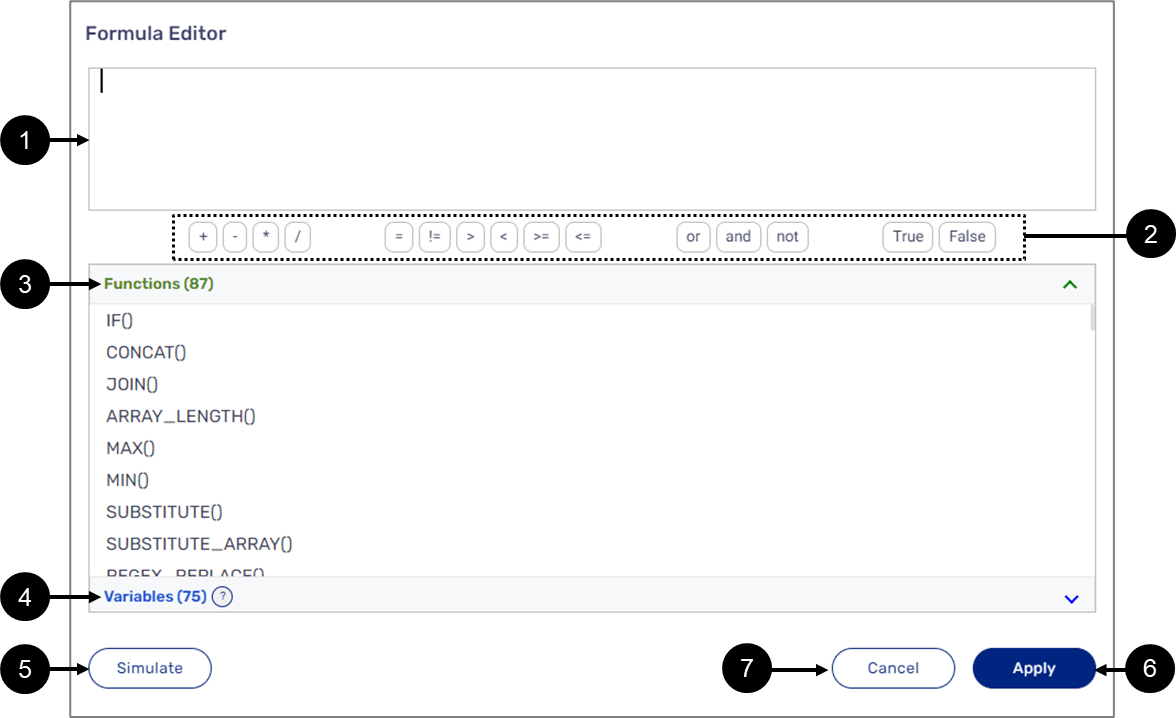
Figure 4: Formula Editor Window
The Formula display window displays the formulas created using the Formula editor. When clicking it or the Edit Formula button, the Edit Formula window appears.
Table 1: Formula Editor Window
| Number | Name | Description |
| 1 | Formula Editor | Enables creation of logical expressions, conditions, and calculations by using built-in operators, functions, and variables |
| 2 | Operators | Enables usage of built-in operators, the operators are divided according to the following categories:
NOTE For a detailed description of operators' behaviors, see the Formula Behaviors section. |
| 3 | Functions | Enables usage of built-in functions NOTE For detailed information about built-in functions, see the Functions section |
| 4 | Variables | Enables usage of variables NOTE
|
| 5 | Simulate | Enables usage of a simulator to simulate functions NOTE For additional information about the simulator see the Formula Editor Simulator section. |
| 6 | Apply | Applies the created logical expressions, conditions, and calculations NOTE If the Formula Editor displays errors, the Apply button will be disabled until the errors are fixed |
| 7 | Cancel | Cancels any changes and closes the Formula Editor Window |
Variables
(See Figure 5)
Variables are the Model's Transaction data items (1) and Metadata items (2). They are used as input/output parameters when creating a formula. Each data item and Metadata item has a specific type (3) that defines their usage as a variable in the formula editor:
- object
- string
- boolean
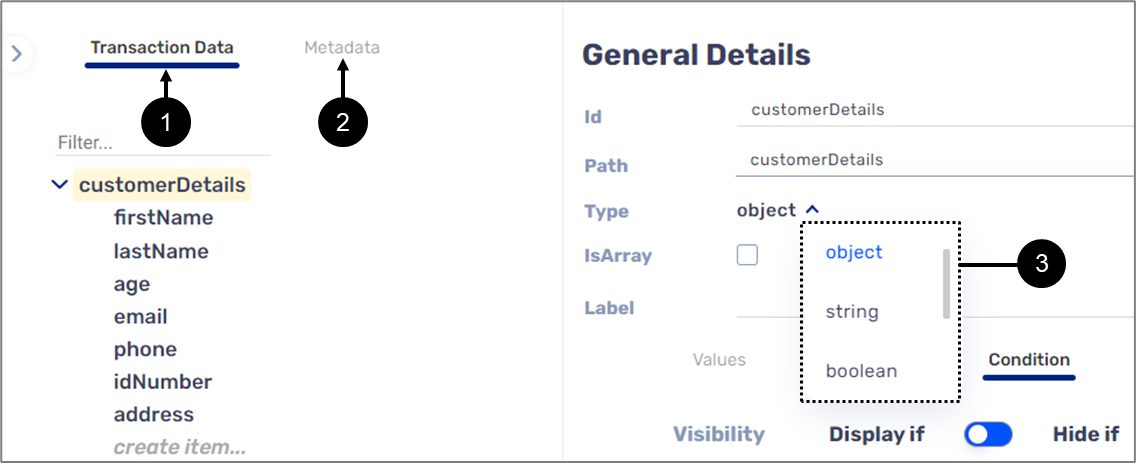
Figure 5: Transaction Data and Metadata
Object Type Variables
Object type variables nest other variables to create a logical data structure. Figure 6 displays a simple data structure in which customerDetails (1) is an object type variable that nests two other variables, firstName and lastName (2). In this type of data structure hierarchy, customerDetails is the parent variable and the variables inside of it are its children.
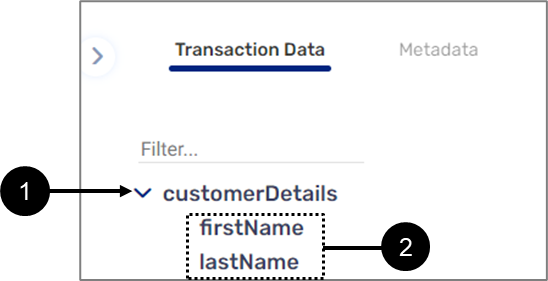
Figure 6: Data Structure
String Type Variable
When creating a formula, string type variables are used as a function's string type parameters or as a returned string type value. For formulas that contain functions such as MAX(), MIN(), or GREATER_THAN(), string type variables are automatically converted into a number variable.
Boolean Type Variable
When creating a formula, boolean type variables are used as a function's True/False parameters or as a returned True/False value.
How to add variables?
(See Figure 7)
Variables can be added to a formula in three different ways:
- Clicking a variable (1).
- Hovering above a variable and then clicking Use (2).
- Manually writing the name of a variable inside the formula editor (3).
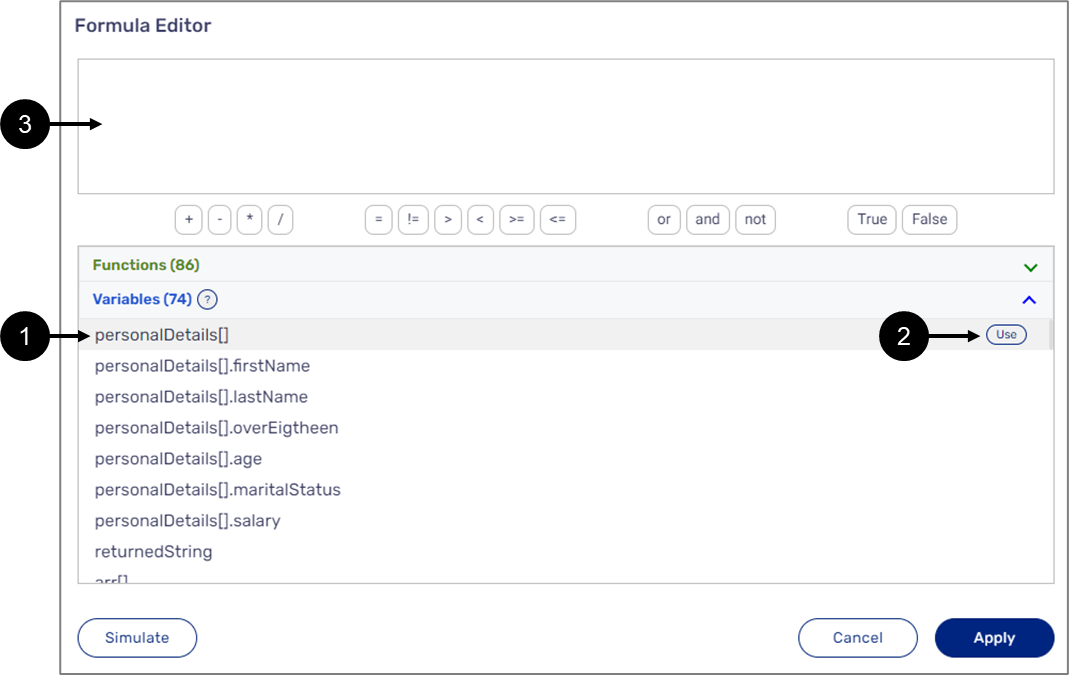
Figure 7: Adding Variables
When adding the variable by clicking it or with the Use button, it will be added in the following format: $variableName. For example: $age (1) or $customerDetails.age (2) if the variable is nested inside an object (see Figure 8):
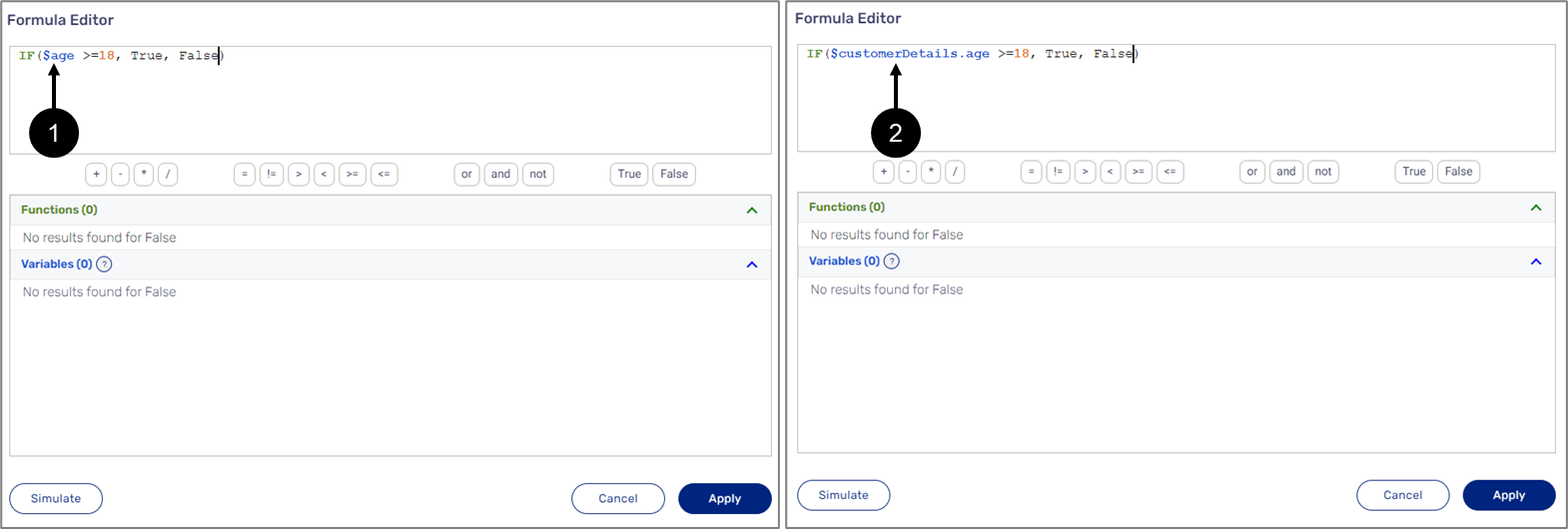
Figure 8: Added Variables
Manually adding Variables
(See Figure 9)
When manually adding a variable, the $ sign must be added manually as well. In addition, when starting to type the name of a variable, the list of available variables (1) updates with each typed letter to display the number of matching results (2). The variable displays an error indication (3) until it is written properly - $+full name (4).
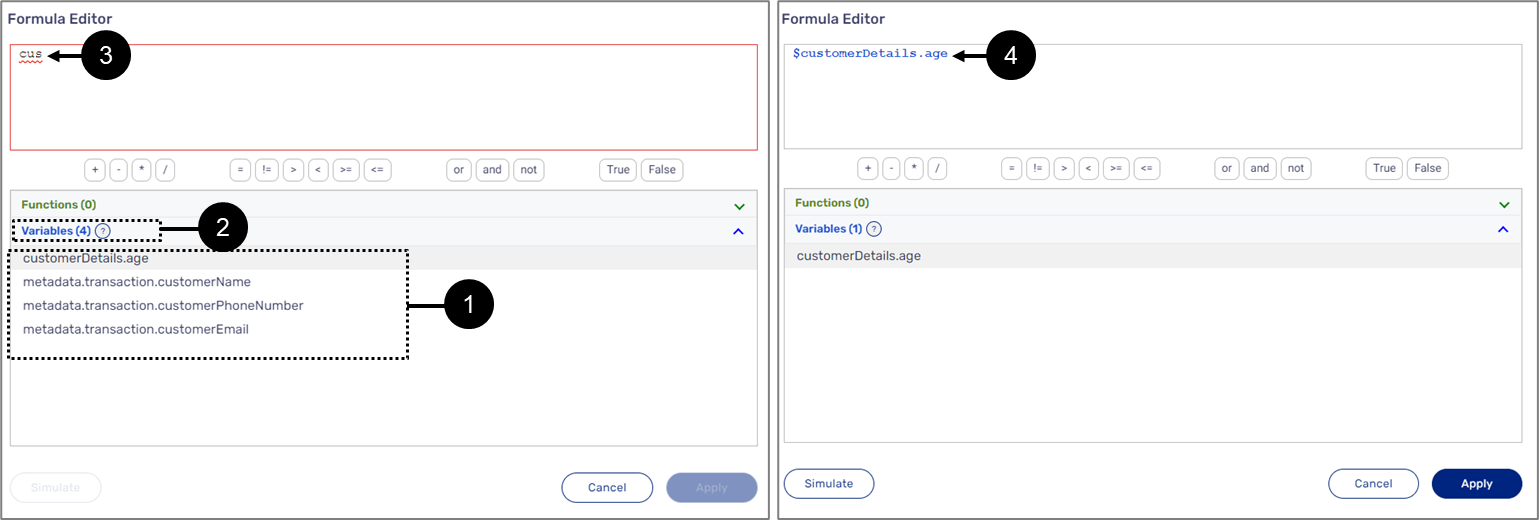
Figure 9: Manually Adding Variables
Manually Adding Nested Variables
Nested variables can be added manually using two methods:
- Full path - by specifying the parent variable, for example, $customerDetails.age.
- Relative path - by writing dots (..) to access the variable without specifying the parent variable, for example, $..age.
Array Type Variables
An Array can be a string type or a boolean type variable that contains zero or more items of the same type. An Array can also be an object type variable nesting other variables that are used as its items. To set any variable as an Array, the IsArray checkbox (1) must be checked (see Figure 10):
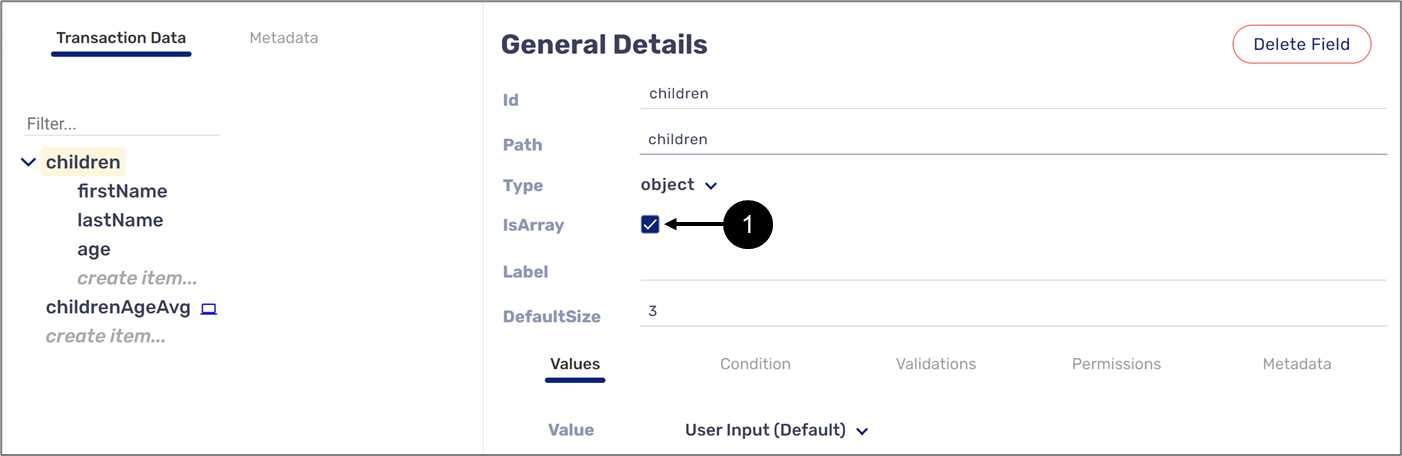
Figure 10: IsArray Checkbox
Accessing Array Items - String/Boolean
The items of a string or boolean type Array are accessed by specifying their path and their index location. For example, Figure 11 displays a string type Array named carsPrice (1):
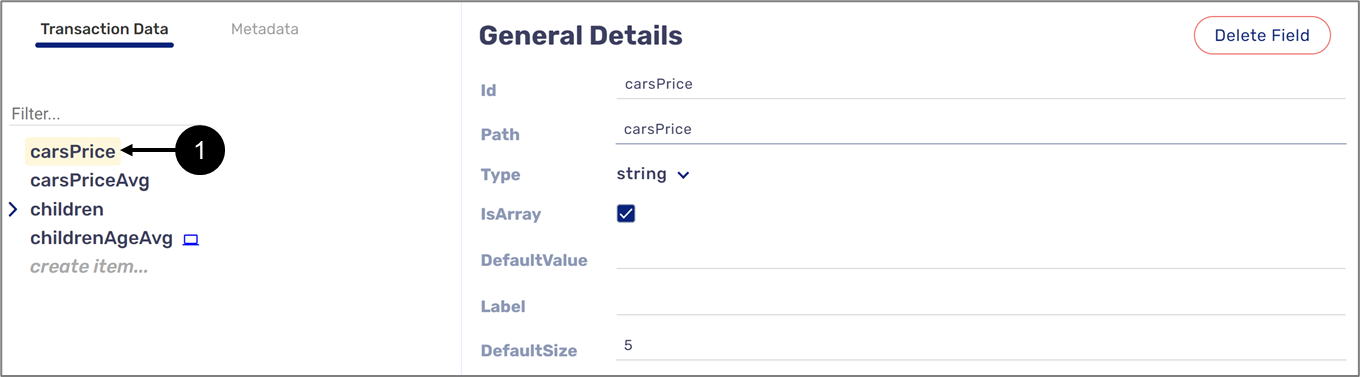
Figure 11: Array Type Variable
When creating a formula, all Array items can be accessed by writing the variable name followed by an asterisk that is written between two square brackets, for example, carsPrice[*] (1). A specific item will be accessed by indicating its index starting from 0, for example, carsPrice[0[ to access the first item and carsPrice[1] to access the second item (2) (see Figure 12):
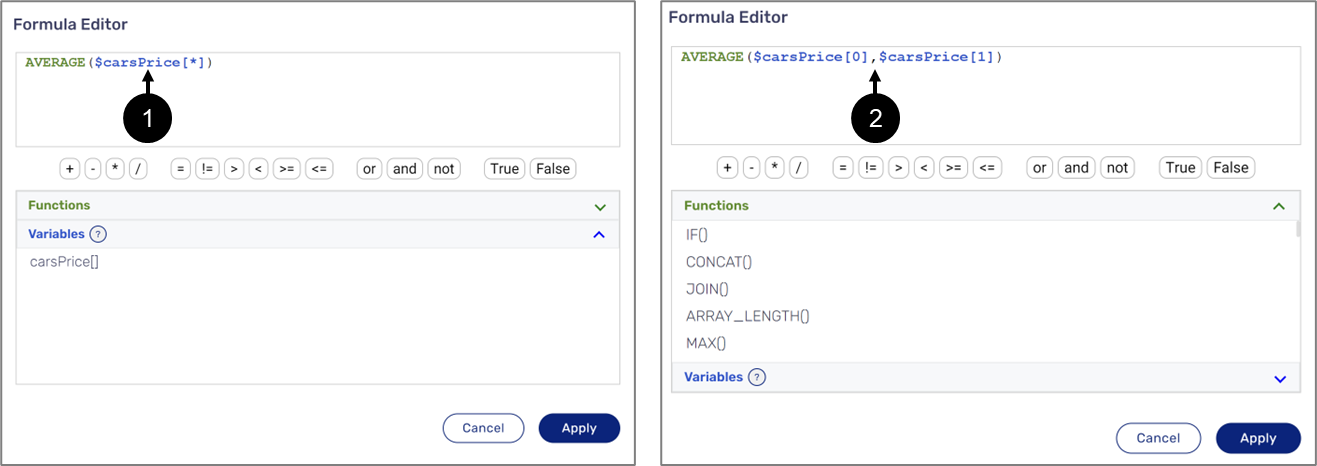
Figure 12: Accessing Array Type Variable Items
Accessing Object Type Array Items
Figure 13 displays an object type Array named children (1) that nests three string type variables (2) used as its items. The childrenAgeAvg variable (3) will be used to create a formula that calculates the average age value from the children Array:
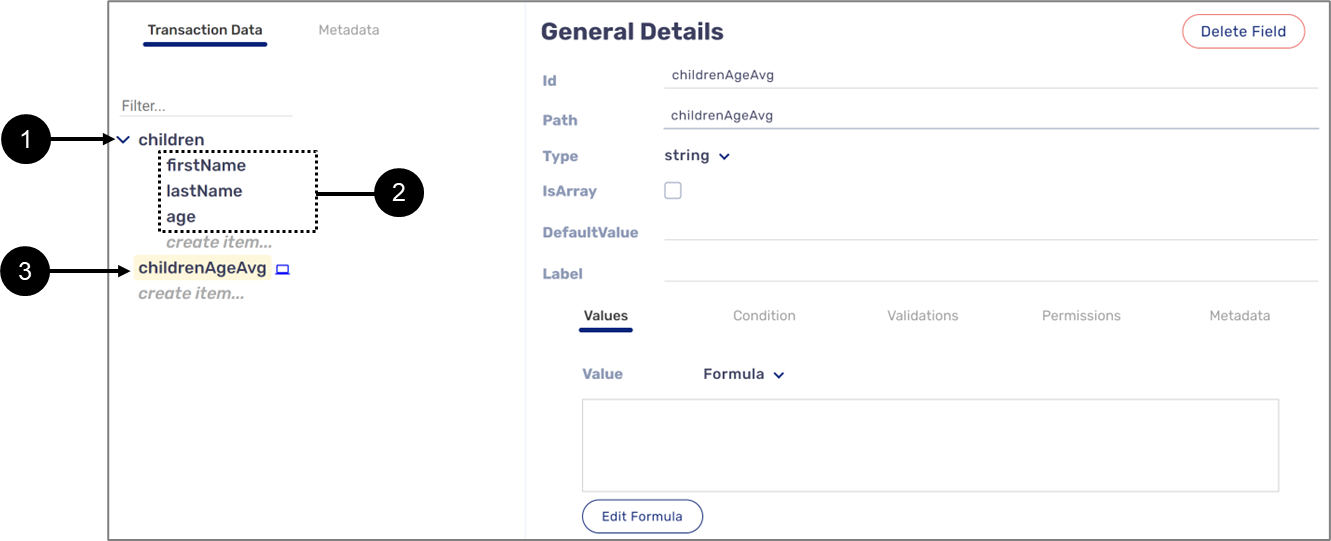
Figure 13: Variables
When creating a formula, all age items within the Array will be accessed by writing $children[*].age (1). A specific item will be accessed by indicating its index starting from 0, for example, children[0].age to access the first item and children[1].age to access the second item (2) (see Figure 14):
![When creating a formula, all age items within the Array will be accessed by writing $children[*].age. A specific item will be accessed by indicating its index starting from 0, for example, children[0].age to access the first item and children[1].age to access the second item.](https://cdn.document360.io/45e1a1b1-1964-46f1-939e-f40bde9b50fa/Images/Documentation/for-inbar-image-4ud01mol.png)
Figure 14: Accessing Object Type Array Items
Nested variables inside an object type Array can be added manually using two methods
- Full path - by specifying the parent variable, for example, $children[].firstName.
- Relative path - by writing dots (..) to access the variable without specifying the parent variable, for example, $..firstName.
Functions
The Formula Editor window contains 86 unique functions:
- ALL() - this function checks if all the provided reference items meet a specific criterion according to a comparison operator.
- AND() - this function checks if all provided parameters are logically true.
- ANY() - this function checks if any of the provided reference items meet a specific criterion according to a comparison operator.
- AVERAGE() - this function returns the numerical average of values in a dataset.
- ARRAY_LENGTH() - this function returns the length of an Array.
- CONCAT() - this function appends string values.
- COUNT() - this function counts the number of values in a dataset.
- COUNT_IF() - this function counts the number of values in a dataset that match a set condition.
- COUNT_UNIQUE - this function counts the number of unique values in a list of specified values and ranges.
- DATE() - this function converts numbers into a date.
- DATE_ADD() - this function adds or subtracts a specified time unit to a date.
- DATE_ADD_ EXACT() - this function adds or subtracts months from date.
- DATE_DIFF() - this function calculates the number of days, months, or years between two dates.
- DATE_FORMAT() - this function converts a provided date to a string, according to conventional datetime formatting.
- DAY() - this function returns the day of a specific date according to a format.
- DIVIDE() - this function returns the quotient of two value
- EQUAL() - this function checks if two values are equal.
- FILTER() - this function filters items according to criteria.
- FORMAT_TIN() - this function converts a 9-digit number to a Taxpayer Identification Number (TIN) format.
- FORMAT_PRECISION() - this function formats a number to a given precision.
- FORMAT_SSN() - this function converts a 9-digit number to a Social Security Number (SSN) format.
- FORMAT_THOUSANDS() - this function formats a number by adding commas.
- FORMAT_CUSTOM() - this function converts and formats text according to a specified pattern.
- GREATER_THAN() - this function checks if the first value is greater than the second value.
- GREATER_THAN_EQUAL() - this function checks if the first value is greater than or equal to the second value.
- IF() - this function checks if a logical expression is true or false.
- IF_ARRAY() - this function checks if a logical expression is true or false.
- INDEX() - this function checks what is the position of the first item that matches the search criteria.
- IS_BETWEEN() - this function checks if a number is included between two numbers.
- IS_BOOLEAN() - this function checks if the type of the input parameter is boolean.
- IS_EMPTY() - this function checks if a variable contains an empty value or not.
- IS_EMPTY_ARRAY() - this function checks if an Array is empty.
- IS_EVEN() - this function checks if the type of the value of the input parameter is even.
- IS_NUMBER() - this function checks if the type of the input parameter is a number.
- IS_ODD() - this function checks if the type of the value of the input parameter is odd.
- IS_TEXT() - this function checks if the type of the input parameter is a text.
- JOIN() - this function appends string values between a separator.
- LENGTH() - this function indicates the length of an input text.
- LESS_THAN() - this function checks if the first value is lower than the second value.
- LESS_THAN_EQUAL() - this function checks if the first input value is lower than or equal to the second input value.
- LN() - this function returns the natural logarithm of a value.
- LOOKUP() - this function looks for a value in a search array and returns the value of the corresponding item (in the same position/index) of a result array.
- LOOKUP_ARRAY() - this function looks for a value in a search array and returns multiple values of the corresponding item (in the same position/index) of a result array.
- LOWER() - this function converts the characters of the input text from uppercase to lowercase.
- LOWER_ARRAY() - this function converts characters of an input Array from uppercase to lowercase.
- MAX() - this function returns the maximum value from a list of numbers, ignoring empty values.
- MIN() - this function returns the minimum value from a list of numbers, ignoring empty values.
- MONTH() - this function returns the month of a specific date according to a format.
- MULTIPLY() - this function returns the multiplication product of two numbers.
- NOT() - this function returns the opposite value of a boolean input.
- NOT_EQUAL() - this function checks if two values are not equal.
- OR() - this function returns False if any of the provided arguments are logically True, and False if all the provided arguments are logically False.
- PAD() - this function adds padding to a string up to the output length.
- PAD_ARRAY() - this function adds padding to all string type Array items up to their output length.
- POSITION() - this function returns the position at which a string/array is first found within text.
- POWER() - this function returns an exponential number (raised to a power).
- PROPER() - this function capitalizes the first character of a word in a specified string and converts the following characters to lowercase.
- RAND_BETWEEN() - this function returns a uniformly random integer between two values, inclusive of those values.
- REGEX_EXTRACT() - this function extracts matching substrings according to a regular expression.
- REGEX_MATCH() - this function checks whether a portion of text matches a regular expression.
- REGEX_REPLACE() - this function replaces matching substrings according to a regular expression.
- REMOVE_EMPTY() - this function removes empty strings and null values from an Array.
- REPLACE() - this function replaces a portion of a text with a different text.
- ROUND() - this function rounds a number to a certain number of decimal places according to standard rules.
- SUBSTITUTE() - this function replaces existing text with new text in a string.
- SUBSTITUTE_ARRAY() - this function replaces existing text with new text in a string for all items in an array.
- SPLIT() - this function splits one string into an array of strings.
- SQRT() - this function returns the square root of a positive number.
- SUBSTRING() - this function returns a segment of a string. Beginning with the start index and up to a specific length.
- SUBTRACT() - this function returns the difference (subtraction result) of two numbers.
- SUM() - this function returns the sum of multiple numbers. Equivalent to the `+` operator.
- SUM_IF() - this function returns a conditional sum across a range.
- SWITCH() - this function checks a value against cases and returns a matching single value result.
- SWITCH_ARRAY() - this function checks a value against cases and returns a matching array result.
- TO_ARRAY() - this function converts a provided set of values into an Array.
- TO_NUM() - this function converts a string to a number.
- TO_TEXT() - this function converts a value to a string.
- TRIM() - this function removes leading and tailing padding elements in a string.
- TYPE() - this function returns the type of value/variable that was entered into the function.
- UNIQUE() - this function returns the unique items of an Array.
- UPPER() - this function converts the characters of the input text from lowercase to uppercase.
- UPPER_ARRAY() - this function converts characters of an input Array from lowercase to uppercase.
- VALUE() - this function returns a value from an Array according to the provided position.
- WEEK_DAY() - this function returns a number representing the day of the week of the date provided (Sunday=1).
- WEEK_NUM() - this function returns a number representing the week of the year of the date provided.
- YEAR() - this function returns the year of a specific date according to a format.
ALL()
The following sections describe the ALL(operator, criteria, reference_items) function.
General Description
This function checks if all the provided reference items meet a specific criterion according to a comparison operator.
Input and Output
Input:
The function receives the following input parameters:
- operator (string):
- "="
- "!="
- ">"
- "<"
- ">="
- "<="
- criteria and reference_items (string, number, boolean):
- Arrays or Array items - for example: $children[*], $children[*].age, $children[0].age.
- Variables - for example: $myAge or $spouseAge.
- Fixed values - for example: "word", 80, True.
- A returned value from a different function - for example: SUM() or IS_BOOLEAN().
Output:
The function returns a boolean value (True or False).
Examples:
Table 2: Inputs/Outputs
| Input | Output |
| ALL(">=", 18, $childrenAge[*]) | If the value of each item in the childrenAge Array equals or bigger than 18 the returned value is True, else False |
| ALL("=", True, kidsStatus[*]) | If the value of each item in the kidsStatus Array equals True the returned value is True, else False |
| ALL("<", $num4, $num1,$num2,$num3) | If the value of each variable: num1,num2, and num3 is smaller than the value of the num4 variable the returned value is True, else False |
| ALL("=", $num4, SUM($num1,$num2,$num3)) | If the returned value of the SUM() function equals the value of the num4 variable the returned value is True, else False |
AND()
The following sections describe the AND(logical_formulas) function.
General Description
This function checks if all provided parameters are logically true.
Input and Output
Input:
The function receives multiple boolean type values or a boolean type Array as input parameters:
- Array or Array items - for example: $haveChildren[*], $children[*].overEighteen, $children[0].overEighteen.
- Variables - for example: $isMarried or $carOwner.
- Fixed values.
- A returned boolean value from a different function - for example: ALL().
Output:
The function returns a boolean value (True or False).
Examples:
Table 3: Inputs/Outputs
| Input | Output |
| AND($haveChildren[*]) | If the value of each item in the haveChildren Array equals True the returned value is True, else False |
| AND($overEighteen [*]) | If the value of each item in the overEighteen Array equals True the returned value is True, else False |
| AND($isMarried) | If the value of the isMarried variable equals true the returned value is True, else False |
| AND("<",$num4, MIN($num1,$num2,$num3)) | If the returned value of the ALL() function equals True the returned value is True, else False |
ANY()
The following sections describe the ANY(operator, criteria, reference_items) function.
General Description
This function checks if any of the provided reference items meet a specific criterion according to a comparison operator.
Input and Output
Input:
The function receives the following input parameters:
- operator (string):
- "="
- "!="
- ">"
- "<"
- ">="
- "<="
- criteria and reference_items (string, number, boolean):
- Arrays or Array's items - for example: $children[*], $children[*].age, $children[0].age.
- Variables - for example: $myAge or $spouseAge.
- Fixed values - for example: "word", 80, True.
- A returned value from a different function - for example: SUM() or IS_BOOLEAN().
Output:
The function returns a boolean value (True or False).
Examples:
Table 4: Inputs/Outputs
| Input | Output |
| ANY(">=", 18, $childrenAge[*]) | If the value of any item in the childrenAge Array equals or bigger than 18 the returned value is True, else False |
| ANY("=", True, kidsStatus[*]) | If the value of any item in the kidsStatus Array equals True the returned value is True, else False |
| ANY("<", $x, $z,$y,$w) | If the value of any variable: num1,num2, or num3 is smaller than the value of the num4 variable the returned value is True, else False |
| ANY("=", $num7, SUM($x,$y,$z), SUM($a,$b,$c)) | If the returned value of any of the SUM() functions equals the value of the num7 variable the returned value is True, else False |
AVERAGE()
The following sections describe the AVERAGE(items) function.
General Description
This function returns the numerical average of values in a dataset.
Input and Output
Input:
The function receives a number type Array or multiple number variables/values as input parameters (items):
- Arrays or Array items - for example: $salary[*], $children[*].age, $children[0].age, $salary[1].
- Variables - for example: $Age or $spouseAge.
- Fixed values.
- A returned value from a different function - for example: SUM() or MIM().
Output:
The function returns a number.
Examples:
Table 5: Inputs/Outputs
| Input | Output |
| AVERAGE($age[*]) | The function returns the average value of the age Array values |
| AVERAGE($num1, $num2, 5, $salary[0],100) | The function returns the average value of the provided variables and fixed values |
| AVERAGE(SUM($num1, $num2), MAX($salary, $spouseSalary)) | The function returns the average value of the returned values from the SUM() and MAX() functions |
ARRAY_LENGTH()
The following sections describe the ARRAY_LENGTH(array) function.
General Description
This function returns the length of an Array.
Input and Output
Input:
The function receives any type of array (boolean, object, string) as an input parameter, for example:
- customer[*].firstName
- $children[*].
- TO_ARRAY("1","2","3","4","5").
- TO_ARRAY($num1,$num2,$num3,$num4,$num5).
Output:
The function returns a number, the length of the Array.
Examples:
Table 6: Inputs/Outputs
| Input | Output |
| ARRAY_LENGTH($children[*]) | The function returns the length of the children Array |
| ARRAY_LENGTH(TO_ARRAY("1","2","3","4","5")) | The function returns the length of the Array that was created with the TO_ARRAY function |
| ARRAY_LENGTH(TO_ARRAY($x,$y,$z)) | The function returns the length of the Array that was created with the TO_ARRAY function |
CONCAT()
The following sections describe the CONCAT(strings_to_concat) function.
General Description
This function appends string values.
Input and Output
Input:
The function receives multiple strings as input parameters:
- A string item of an object type Array - for example: $children[*].firstName, $children[0].firstName.
- A string type Array - for example: $colors[*].
- A string item of a string type Array - for example: $color[0] or $color[1].
- Fixed values.
- Variables - for example: $word1, $word2, $word3.
- A function that returns a string value, for example: TO_TEXT().
Output:
The function returns a single appended string.
Examples:
Table 7: Inputs/Outputs
| Input | Output |
| CONCAT($firstName[*]) For example: $firstName[0] = "ronny" $firstName[1] = "dana" $firstName[2] = "dee" | The function returns a single appended string value, comprised of the string values of the firstName Array, for example: "ronnydanadee" |
| CONCAT("1 ","2","3","4","5") | The function returns a single appended string value, comprised of the values of the provided fixed strings, for example: "1 2345" |
| CONCAT($word1,$word2,$word3) For example: $word1 = "purple" $word2 = "yellow" $word3 = "blue" | The function returns a single appended string value, comprised of the values of the provided string variables, for example: "purpleyellowblue" |
COUNT()
The following sections describe the COUNT(items) function.
General Description
This function counts the number of values in a dataset.
Input and Output
Input:
The function receives an Array or multiple variables/values of any type (string, number, boolean, object, date) as input parameters (items):
- An object type Array - for example: $children[*].
- A string item of an object type Array - for example: $children[*].firstName, $children[0].firstName.
- A string type Array - for example: $colors[*].
- A string item of a string type Array - for example: $color[0], $color[1].
- Fixed values - for example: "Word",1, True, 12/03/1985.
- Variables - for example: $var1, $var2, $var3.
- A function that returns any type of value - for example: TO_DATE(), IS_BOOLEAN(), SUM().
Output:
The function returns a number.
Examples:
Table 8: Inputs/Outputs
| Input | Output |
| COUNT($firstName[*]) For example: $firstName[0] = "ronny" $firstName[1] = "dana" $firstName[2] = "dee" | The function counts the number of values in the firstName Array and returns a number, for example: 3 |
| COUNT("Word",2, True, 01/05/1985) | The function counts the number of fixed values and returns a number, for example: 4 |
| COUNT($var1,$var2, $var3) For example: $var1 = "purple" $var2 = False $var3 = 5 | The function counts the number of input variables values and returns a number, for example: 3 |
| COUNT(SUM(6,7), IS_BOOLEAN($isMarried)) | The function counts the number of returned values from input functions and returns a number, for example: 2 |
COUNT_IF()
The following sections describe the COUNT_IF(operator, condition_value, items) function.
General Description
This function counts the number of values in a dataset that match a set condition.
Input and Output
Input:
The function receives the following input parameters:
- operator (string):
- "="
- "!="
- ">"
- "<"
- ">="
- "<="
- condition_value and items (string, number, boolean):
- Array or Array items - for example: $children[*], $children[*].age, $children[0].age.
- Variables - for example: $myAge or $spouseAge.
- Fixed values - for example: "word", 80, True.
- A returned value from a different function - for example: SUM() or IS_BOOLEAN().
Output:
The function returns a number.
Examples:
Table 9: Inputs/Outputs
| Input | Output |
| COUNT_IF("=", "Dennis", $firstName[*] ) For example: $children[0].firstName = "Ronny" $children[1].firstName = "Dana" $children[2].firstName = "Dennis" | The function counts the number of values in the firstName Array that match the string "Dennis" and returns a number, for example: 1 |
| COUNT_IF("<", 1000, $var1,$var2,$var3) For example: $var1 = 500 $var2 = 5000 $var3 = 2000 | The function counts the number of input variables values that are lower than 1000 and returns a number, for example: 1 |
| COUNT_IF("=", $number, SUM($num1,$num2), MAX($num3,$num4)) For example: $Number = 15 $num1 = 8 $num2 = 7 $num3 = 15 $num4 = 9 | The function counts the number of returned values from input functions that are equal to the value of the number variable and returns a number, for example: 2 |
COUNT_UNIQUE()
The following sections describe the COUNT_UNIQUE(items) function.
General Description
This function counts the number of unique values in a list of specified values and ranges.
Input and Output
Input:
The function receives an Array or multiple variables/values of any type (string, number, boolean, object, date) as input parameters (items):
- An object type Array - for example: $children[*].
- Array items - for example: $children[*].firstName, $children[0].firstName.
- A string type Array - for example: $colors[*].
- A boolean type Array - for example: $isMarried[*].
- String and boolean Array items - for example: $color[0], $isMarried[1].
- Fixed values - for example: "Word",1, True, 12/03/1985.
- Variables - for example: $var1, $var2, $var3.
- A function that returns any type of value - for example: IS_BOOLEAN(), SUM().
Output:
The function returns a number.
Examples:
Table 10: Inputs/Outputs
| Input | Output |
| COUNT_UNIQUE ("=", "Dennis", $firstName[*] ) For example: $children[0].firstName = "Ronny" $children[1].firstName = "Dana" $children[2].firstName = "Dennis" | The function counts the number of unique values in the firstName Array and returns a number, for example: 3 |
| COUNT_UNIQUE("Word",2, True, 01/05/1985) | The function counts the number of unique fixed values and returns a number, for example: 4 |
| COUNT_UNIQUE ($var1,$var2, $var3) For example: $var1 = "purple" $var2 = False $var3 = False | The function counts the number of unique input variables values and returns a number, for example: 2 |
| COUNT_UNIQUE(SUM(6,7), IS_BOOLEAN($isMarried)) | The function counts the number of unique returned values from input functions and returns a number, for example: 2 |
DATE()
The following sections describe the DATE(year, month, day) function.
General Description
This function converts numbers into a date format.
Input and Output
Input:
The function receives three input type number parameters:
- year- for example 1985.
- month - for example 05.
- day - for example 01.
Output:
The function returns a date.
Because the function returns a date value, it must be wrapped in the DATE_FORMAT() function to return a string. For additional information about the DATE_FORMAT() function, click here.
Examples:
Table 11: Inputs/Outputs
| Input | Output |
| DATE_FORMAT(DATE(1985,5,1),"yyyy-MM-dd") | The function returns a date in the following format: 1985-05-01 |
| DATE_FORMAT(DATE(1985,5,1),"dd-MM-yyyy") | The function returns a date in the following format: 01-05-1985 |
| DATE_FORMAT(DATE(1985,5,1),"d-M-Y") | The function returns a date in the following format: 1-5-1985 |
| DATE_FORMAT(DATE(1985,5,1),"d-M-yy") | The function returns a date in the following format: 1-5-85 |
| DATE_FORMAT(DATE(1985,5,1),"dd-MMM-yy") | The function returns a date in the following format: 01-May-85 |
DATE_ADD()
The following sections describe the DATE_ADD(date, add, date_unit) function.
General Description
This function adds or subtracts a specified time unit to a date.
Input and Output
Input:
The function receives three input parameters:
- date - a date value returned from a different function, for example: DATE(1985,05,01).
- add:
- A fixed number - for example: 8 or -5.
- A string type variable - for example: $number or $dates[0].items.
- date_unit:
- A fixed string - for example: "Y", "M", "D".
- A string type variable, for example: $dateUnit or $date[0].dateUnit
Output:
The function returns a date.
Because the function returns a date value, it must be wrapped in the DATE_FORMAT() function to return a string. For additional information about the DATE_FORMAT() function, click here.
Examples:
Table 12: Inputs/Outputs
| Input | Output |
| DATE_FORMAT(DATE_ADD(DATE(2022, 05, 01),$number ,"Y"),"yyyy-MM-dd") For example: $number = 8 | The function returns a date in the following format: 2030-05-01 |
| DATE_FORMAT(DATE_ADD(DATE(1985, 05, 01),$date[0].number ,"D"),"yyyy-MM-dd") For example: $date[0].number = 8 | The function returns a date in the following format: 1985-05-09 |
DATE_ADD_EXACT_MONTHS()
The following sections describe the DATE_ADD_EXACT_MONTHS(date, add) function.
General Description
This function adds or subtracts a specified time unit to a date.
Input and Output
Input:
The function receives three input parameters:
- date - a date value returned from a different function, for example: DATE(1985,05,01).
- add:
- A fixed number - for example: 8 or -5.
- A string type variable - for example: $number or $dates[0].items.
Output:
The function returns a date.
Because the function returns a date value, it must be wrapped in the DATE_FORMAT() function to return a string. For additional information about the DATE_FORMAT() function, click here.
Examples:
Table 13: Inputs/Outputs
| Input | Output |
| DATE_FORMAT(DATE_ADD_EXACT_MONTHS(TO_DATE("2022-07-31", "yyyy-MM-dd"), 2)) | The function returns a date in the following format: 2022-09-30, the last day of September |
DATE_DIFF()
The following sections describe the DATE_DIFF(start_date, end_date, date_unit) function.
General Description
This function calculates the number of days, months, or years between two dates.
Input and Output
Input:
The function receives three input parameters:
- start_date/end_date - a date value returned from a different function, for example: DATE(1985,05,01).
- date_unit:
- A fixed string - for example: "Y", "M", "D".
- A string type variable, for example: $dateUnit, $date[0].dateUnit
Output:
The function returns a number.
Examples:
Table 14: Inputs/Outputs
| Input | Output |
| DATE_FORMAT(DATE_DIFF(DATE(1985, 5,1 ),DATE(2022, 18, 09), $dateUnit) For example: $dateUnit = "Y" | The function returns a number: 37. |
DATE_FORMAT()
The following sections describe the DATE_FORMAT(date, format) function.
General Description
This function converts the provided date to a string, according to conventional datetime formatting.
Input and Output
Input:
The function receives two input parameters:
- date - a date value returned from a different function, for example: DATE(1985,05,01).
- format - comprised of a month, day, and year. For example:
- "d/M/y" or "d-M-y" - (1/5/85 or 1-5-85).
- "dd/MM/yy" or "dd-MM-yy" (01/05/85 or 01-05-85).
- "ddd/MMM/yyyy" or "ddd-MMM-yyyy" (Mon/Feb/1985 or Mon-Feb-1985).
- "dddd/MMMM/yyyy" or "dddd-MMMM-yyyy" (Monday/February/1985 or Monday/February/1985).
Output:
The function returns a string.
Examples:
Table 15: Inputs/Outputs
| Input | Output |
| DATE_FORMAT(DATE(1985,5,1),"yyyy-MM-dd") | The function returns a date in the following format: 1985-05-01 |
| DATE_FORMAT(DATE(1985,5,1),"dd-MM-yyyy") | The function returns a date in the following format: 01-05-1985 |
| DATE_FORMAT(DATE(1985,5,1),"d-M-Y") | The function returns a date in the following format: 1-5-1985 |
| DATE_FORMAT(DATE(1985,5,1),"d-M-yy") | The function returns a date in the following format: 1-5-85 |
| DATE_FORMAT(DATE(1985,5,1),"dd-MMM-yy") | The function returns a date in the following format: 01-May-85 |
DAY()
The following sections describe the DAY(date) function.
General Description
This function returns the day of a specific date according to a format.
Input and Output
Input:
The function receives a date parameter returned from a different function, for example:
- DAY(TO_DATE($customer[0].dateBirth, "yyyy-dd-MM")).
- DAY(DATE(1985/05/01)).
Output:
The function returns a number.
Examples:
Table 16: Inputs/Outputs
| Input | Output |
| DAY(TO_DATE($date, "yyyy-MM-dd")) For example: $date = 1985-01-05 | The function returns a day according to the format: 05 |
| DAY(TO_DATE($date, "yyyy-dd-MM")) For example: $date = 1985-01-05 | The function returns a day according to the format: 01 |
| DAY(DATE(1985,03,12)) | The function returns a day according to the format of the DATE function: 12 |
DIVIDE()
The following sections describe the DIVIDE(value1, value2) function.
General Description
This function returns the quotient of two values
Input and Output
Input:
The function receives two number type input parameters:
- Array items - for example: $children[0].age or $salary[1].
- Variables - for example: $Age or $spouseAge.
- Fixed values.
- A returned value from a different function - for example: SUM() or MIM().
Output:
The function returns a number.
Examples:
Table 17: Inputs/Outputs
| Input | Output |
| DIVIDE($num1, $num2) | The function returns the quotient of the provided variables |
| DIVIDE(SUM($num1, $num2), MAX($salary, $spouseSalary)) | The function returns the quotient of the returned values from the SUM() and MAX() functions |
EQUAL()
The following sections describe the EQUAL(value1, value2) function.
General Description
This function checks if two values are equal.
Input and Output
Input:
The function receives two input parameters from any type (number, string, boolean, date):
- Array items - for example: $children[1] or $children[0].age
- Variables - for example: $number1, $isMarried.
- Fixed values - for example: "True", True, 8.
- Returned values from different functions - DATE(), SUM(), ANY().
Output:
The function returns a boolean value (True or False).
Examples:
Table 18: Inputs/Outputs
| Input | Output |
| EQUAL(DATE(2022,01,05), DATE(2022,06,07)) | The function returns a boolean value: False |
| EQUAL($children[0].FirstName, "Dana") For example: $children[0].firstName = "Ronny" | The function returns a boolean value: False |
| EQUAL($number, 8) For example: $number = 8 | The function returns a boolean value: True |
FILTER()
The following sections describe the FILTER(operator, search_key, search_items) function.
General Description
This function filters items according to criteria.
Input and Output
Input:
The function receives the following input parameters:
- operator (string):
- "="
- "!="
- ">"
- "<"
- ">="
- "<="
- search_key and search_items (string, number, boolean):
- Arrays or Array items - for example: $children[*], $children[*].age, $children[0].age.
- Variables - for example: $myAge or $spouseAge.
- Fixed values - for example: "word", 80, True.
- A returned value from a different function - for example: SUM() or IS_BOOLEAN().
Output:
The function returns an array of values.
- Because the function returns an array of values, it must be wrapped in a function such as JOIN() or CONCAT(), and in addition, all its variables or fixed values must be string type.
- For additional information about the JOIN() function, click here.
- For additional information about the Contact() function, click here.
Table 19: Inputs/Outputs
| Input | Output |
| JOIN(FILTER("=",18, age[*]), ",") For example: $age[0] = 18 $age[1] = 12 $age[2] = 10 $age[3] = 18 | The function checks which values form the age Array are equal to the number 18 and returns them, for example: 18,18 |
| JOIN(FILTER(">=",SUM($num1,$num2,$num3), bills[*]), ",") For example: $num1=100 $num2 = 200 $num3 = 300 $bills[0] = 300 $bills[1] = 500 $bills[2] = 600 $bills[3] = 700 $bills[4] = 800 | The function checks which values from the bills Array are equal or greater than the returned number from the SUM() function and returns them, for example: 600,700,800 |
GREATER_THAN()
The following sections describe the GREATER_THAN(value1, value2) function.
General Description
This function checks if the first value is greater than the second value.
Input and Output
Input:
The function receives two input parameters (number or date), for example:
- Variables - $number1 or $number2.
- Fixed number values.
- Returned values from different functions - DATE(), SUM().
Output:
The function returns a boolean value (True or False).
Examples:
Table 20: Inputs/Outputs
| Input | Output |
| GREATER_THAN(DATE(2022,01,05), DATE(2022,01,05)) | The function returns a boolean value: False |
| GREATER_THAN(SUM($num1, $num2, $num3), $number) For example: $number = 300 $num1 = 400 $num2 = 300 $num3 = 100 | The function returns a boolean value: True |
GREATER_THAN_EQUAL()
The following sections describe the GREATER_THAN_EQUAL(value1, value2) function.
General Description
This function checks if the first value is greater than or equal to the second value.
Input and Output
Input:
The function receives two input parameters (number or date), for example:
- Variables - $number1, or $Number2.
- Fixed number values.
- Returned values from different functions - DATE(), SUM().
Output:
The function returns a boolean value (True or False).
Examples:
Table 21: Inputs/Outputs
| Input | Output |
| GREATER_THAN_EQUAL(DATE(2022,01,05), DATE(2022,01,05)) | The function returns a boolean value: True |
| GREATER_THAN_EQUAL(SUM($num1, $num2, $num3), $number) For example: $number = 300 $num1 = 50 $num2 = 100 $num3 = 100 | The function returns a boolean value: False |
IF()
The following sections describe the IF(logical_expression, value_if_true, value_if_false) function.
General Description
This function checks if a logical expression is true or false.
Input and Output
Input:
The function receives three input parameters:
- logical_expression that is comprised of:
- Comparison operators:
- =
- !=
- >
- <
- >=
- <=
- string, boolean, number, or date values:
- Array items - for example: $children[0].firstName, $isMarried[1].
- Variables - for example: $number, $word, $booleanValue.
- Fixed values - for example: 8, "word", True.
- Other functions - for examples: DATE(), SUM(), ALL().
- Comparison operators:
- value_if_true and value_if_false:
- string, boolean, number, or date values:
- Array items - for example: $children[0].firstName, $isMarried[1].
- Variables - for example: $number, $word, $booleanValue.
- Fixed values - for example: 8, "word", True
- Other functions - for examples: DATE(), SUM(), ALL().
- string, boolean, number, or date values:
Output:
The function returns the value_if_true parameter or the value_if_false parameter according to the result of the logical expression.
Examples:
Table 22: Inputs/Outputs
| Input | Output |
| IF(SUM($num1, $num2)>SUM($num3, $num4), True, False) | The function checks if the returned value from the first SUM() function is greater than the returned value from the second SUM() function and returns True or False |
| IF(DATE($year, $month, $day)=DATE($year1, $month1, $day1), True, False) | The function checks if the returned value from the first DATE() function is equal to the returned value from the second DATE() function and returns True or False |
IF_ARRAY()
The following sections describe the IF_ARRAY(logical_expression, value_if_true, value_if_false) function.
General Description
This function checks if a logical expression is true or false.
Input and Output
Input:
The function receives three input parameters:
- logical_expression that is comprised of:
- Comparison operators:
- =
- !=
- >
- <
- >=
- <=
- string, boolean, number, or date values:
- Array items- for example: $children[0].firstName or $isMarried[1].
- Variables - for example: $number, $word, $booleanValue.
- Fixed values - for example: 8, "word", True.
- Other functions - for examples: DATE(), SUM(), ALL().
- Comparison operators:
- value_if_true and value_if_false:
- string or number Arrays, for example:
- $children[*].firstName
- $ages[*].
- TO_ARRAY().
- string or number Arrays, for example:
Output:
The function returns the value_if_true parameter (Array) or the value_if_false parameter (Array) according to the result of the logical expression.
- Because the function returns an array of values, it must be wrapped in a function such as JOIN() or CONCAT(), and in addition, all its variables and fixed values must be string type.
- For additional information about the JOIN() function, click here.
- For additional information about the Contact() function, click here.
Examples:
Table 23: Inputs/Outputs
| Input | Output |
JOIN(IF_ARRAY($carOwner = "yes", TO_ARRAY($year,$color,$carModel)),",") | The function checks if the value of the carOwner variable is equal to "yes" and returns an Array that was created using the TO_ARRAY() function or nothing |
INDEX()
The following sections describe the INDEX(reference_array, search_criteria) function.
General Description
This function checks the position of the first item that matches the search criteria.
Input and Output
Input:
The function receives two input parameters:
- reference_array (string, number, boolean):
- Array or Array items - for example: $kids[*].ages, $isMarried[*], $kids[0].ages, $isMarried[0].
- Variables - for example: $number, $word, $booleanValue.
- Fixed values - for example: 8, "word", True.
- A returned Array from the TO_ARRAY() function.
- search_criteria (string, number, boolean):
- Array items - for example: $kids[0].ages or $isMarried[0].
- Variables - for example: $number, $word, $booleanValue.
- Fixed values - for example: 8, "word", True.
- A returned value from a different function, for example: SUM(), MIN(), AND().
Output:
The function returns a number - the first index/position (starting from 0) of the item that matches the search criteria.
Examples:
Table 24: Inputs/Outputs
| Input | Output |
| INDEX(firstName[*], "Dana") For example: firstName[0] = "Ronny" firstName[1] = "Dana" firstName[2] = "Dee" | The function checks if the firstName Array has a value that matches the string "Dana" and returns its index/position. For example: 1 |
| INDEX(TO_ARRAY($num1, $num2, $num3), $number) For example: $number = "9" $num1 = "6" $num2= "7" $num3= "9" | The function checks if the returned Array from the TO_ARRAY function has an item with a value that matches the value of the number variable and returns its index/position. For example: 2 |
IS_BETWEEN()
The following sections describe the IS_BETWEEN(value_to_compare, lower_number, upper_number, lower_value_is_inclusive, upper_value_is_inclusive) function.
General Description
This function checks if a number is included between two numbers.
Input and Output
Input:
The function receives five input parameters:
- value_to_compare, lower_number, upper_number (number):
- Array items - for example: $kids[0].age or $ages[1].
- Variables - for example: $num1 or $num2.
- Fixed values.
- A returned number from another function, for example: SUM(), MIN(), MAX().
- lower_value_is_inclusive, upper_value_is_inclusive (boolean):
- Array items - for example: $status[0].isMarried or $isMarried[0].
- Variables - for example: $booleanValue.
- Fixed values.
- A returned value from a different function, for example: OR(), ANY(), AND().
Output:
The function returns the boolean value True or the lower_value_is_inclusive parameter if the value_to_compare parameter is between the lower_number and the upper_number parameters. If not, the function will return False or the upper_value_is_inclusive parameter.
Examples:
Table 25: Inputs/Outputs
| Input | Output |
| IS_BETWEEN(SUM($num1,$num2), $lowerNumber, $upperNumber, True, False) | The function checks if returned value from the SUM() function is between the values of the lowerNumber and the upperNumber variables and returns True or False |
| IS_BETWEEN($kidAge, $LowAge, $highAge, $isAgeSuitable, False) | The function checks if the value of the kidAge variable is between the values of the lowAge and the highAge variables and returns the isAgeSuitablevariable or False |
IS_BOOLEAN()
The following sections describe the IS_BOOLEAN(value) function.
General Description
This function checks if the type of the input parameter is boolean.
Input and Output
Input:
The function receives one input parameter of any type (string, number, boolean, date):
- Array items - for example: $status[0].isMarried or $isMarried[0].
- Variables - for example: $variable1 or $variable2.
- Fixed values - for example: "True", True, 8.
- A returned value from a different function, for example: SUM(), DATE(), AND().
Output:
The function returns a boolean value (True or False).
Examples:
Table 26: Inputs/Outputs
| Input | Output |
| IS_BOOLEAN($variable1) | The function checks if the type of the $variable1 parameter is boolean and returns True or False |
IS_EMPTY()
The following sections describe the IS_EMPTY(value) function.
General Description
This function checks if a variable contains an empty value or not.
Input and Output
Input:
The function receives one input parameter of any type (string, number, boolean, date):
- Array items - for example: $status[0].isMarried, $isMarried[0].
- Variables - for example: $word, $number, $isBoolean.
- Fixed values - for example: "True", True, 8.
- A returned value from a different function, for example: SUM(), DATE(), AND().
Output:
The function returns a boolean value (True or False).
Examples:
Table 27: Inputs/Outputs
| Input | Output |
| IS_EMPTY($isMarried) For example: $isMarried = True | The function checks if the value of the $isMarried item from the status Array is empty and returns True or False, for example: True |
IS_EMPTY_ARRAY()
The following sections describe the IS_EMPTY_ARRAY(array) function.
General Description
This function checks if an Array is empty.
Input and Output
Input:
The function receives one input parameter, an Array of any kind (string, boolean, number, date), for example:
- $children[*], $children[*].firstName, $isMarried[*].
- An Array returned from the TO_ARRAY() function.
Output:
The function returns a boolean value (True or False).
Examples:
Table 28: Inputs/Outputs
| Input | Output |
| IS_EMPTY_ARRAY(isMarried[*]) | The function checks if the isMarried Array is empty and returns True or False |
| IS_EMPTY_ARRAY(TO_ARRAY(DATE($year,$month,$day),$boolValue)) | The function checks if all the values returned from the TO_ARRAY() function are empty and returns True or False |
IS_EVEN()
The following sections describe the IS_EVEM(value) function.
General Description
This function checks if the type of the value of the input parameter is even.
Input and Output
Input:
The function receives one number type input parameter:
- Array items - for example: $status[0].isMarried or $isMarried[0].
- Variables - for example: $variable1 or $variable2.
- Fixed values.
- A returned value from a different function, for example: SUM(), MIN(), MAX().
Output:
The function returns a boolean value (True or False).
Examples:
Table 29: Inputs/Outputs
| Input | Output |
| IS_EVEN($variable1) | The function checks if the value of the $variable1 parameter is even and returns True or False |
| IS_EVEN(SUM($num1,$num2,$num3)) | The function checks if the value returned from the SUM() function is even and returns True or False |
IS_NUMBER()
The following sections describe the IS_NUMBER(value) function.
General Description
This function checks if the type of the input parameter is a number.
Input and Output
Input:
The function receives one input parameter of any type (string, number, boolean, date):
- Array items - for example: $status[0].isMarried or $isMarried[0].
- Variables - for example: $variable1 or $variable2.
- Fixed values - for example: "True", True, 8.
- A returned value from a different function, for example: SUM(), DATE(), AND().
Output:
The function returns a boolean value (True or False).
Examples:
Table 30: Inputs/Outputs
| Input | Output |
| IS_NUMBER($variable1) For example: $variable1 = "123456" | The function checks if the type of the $variable1 parameter is number and returns True or False NOTE In this case, $variable1 contains a string with digits only so the returned value is True |
IS_ODD()
The following sections describe the IS_ODD(value) function.
General Description
This function checks if the type of the value of the input parameter is odd.
Input and Output
Input:
The function receives one number type input parameter:
- Array item - for example: $status[0].isMarried or $isMarried[0].
- Variables - for example: $variable1 or $variable2.
- Fixed values.
- A returned value from a different function, for example: SUM(), MIN(), MAX().
Output:
The function returns a boolean value (True or False).
Examples:
Table 31: Inputs/Outputs
| Input | Output |
| IS_ODD($variable1) | The function checks if the value of the $variable1 parameter is odd and returns True or False |
| IS_ODD(SUM($num1,$num2,$num3)) | The function checks if the value returned from the SUM() function is odd and returns True or False |
IS_TEXT()
The following sections describe the IS_TEXT(value) function.
General Description
This function checks if the type of the input parameter is a text.
Input and Output
Input:
The function receives one input parameter of any type (string, number, boolean, date):
- Array items - for example: $status[0].isMarried or $isMarried[0].
- Variables - for example: $variable1 or $variable2.
- Fixed values - for example: "True", True, 8.
- A returned value from a different function, for example: SUM(), DATE(), AND().
Output:
The function returns a boolean value (True or False).
Examples:
Table 32: Inputs/Outputs
| Input | Output |
| IS_TEXT($variable1) For example: $variable1 = 123456 | The function checks if the type of the $variable1 parameter is text and returns True or False, for example: False |
JOIN()
The following sections describe the JOIN(strings_to_join, separator) function.
General Description
This function appends string values between a separator.
Input and Output
Input:
The function receives two string type input parameters:
- Array or Array items - for example: $kids[*].ages, $isMarried[*], $kids[0].ages, $isMarried[0].
- Variables - $word1, $word2, $word3.
- Fixed values.
- A function that returns a string value, for example, DATE_FORMAT() or TO_TEXT().
Output:
The function returns a single appended string.
Examples:
Table 33: Inputs/Outputs
| Input | Output |
| JOIN($firstName[*], ",") For example: $firstName[0] = "ronny" $firstName[1] = "dana" $firstName[2] = "dee" | The function returns a single appended string value, separated by a separator, comprised of the string values of the firstName Array, for example: "ronny","dana","dee" |
| JOIN("1","2","3","4","5","-") | The function returns a single appended string value, separated by a separator, comprised of the values of the provided fixed strings, for example: "1"-"2"-"3"-"4"-"5" |
| JOIN($word1,$word2,$word3, ",") For example: $word1 = purple $word2 = yellow $word3 = blue | The function returns a single appended string value, separated by a separator, comprised of the values of the provided string variables, for example: "purple","yellow","blue" |
| JOIN(DATE_FORMAT(date(2022,05,01, "yyyy-MM-dd)),TO_TEXT(MIN(6,7))," ,") | The function returns a single appended string value, separated by a separator, comprised of the values returned from the DATE_FORMAT() and MIN() functions, for example: "2022-05-01","6" |
LENGTH()
The following sections describe the LENGTH(text) function.
General Description
This function indicates the length of an input text.
Input and Output
Input:
The function receives one string type input parameter, for example:
- Array items - $kids[0].firstName or $color[1].
- Variables - $text1 or $text2.
- Fixed values.
- Returned values from different functions - JOIN() or TO_TEXT().
Output:
The function returns a number.
Examples:
Table 34: Inputs/Outputs
| Input | Output |
| LENGTH(JOIN(TO_ARRAY(DATE_FORMAT(date(2022,7,8), "yyyy-M-d"),TO_TEXT(123456)),",")) | The function returns a number: 15 (2022-7-8,123456) |
LESS_THAN()
The following sections describe the LESS_THAN(value1, value2) function.
General Description
This function checks if the first value is lower than the second value.
Input and Output
Input:
The function receives two input parameters (number or date), for example:
- Variables - $number1 or $number2.
- Fixed number values.
- Returned values from different functions - DATE(), SUM().
Output:
The function returns a boolean value (True or False).
Examples:
Table 35: Inputs/Outputs
| Input | Output |
| LESS_THAN(DATE(2022,01,05), DATE(2022,01,05)) | The function returns a boolean value: False |
| LESS_THAN(SUM($num1, $num2, $num3), $number) For example: $number = 300 $num1 = 400 $num2 = 300 $num3 = 100 | The function returns a boolean value: True |
LESS_THAN_EQUAL()
The following sections describe the LESS_THAN_EQUAL(value1, value2) function.
General Description
This function checks if the first input value is lower than or equal to the second input value.
Input and Output
Input:
The function receives two input parameters (number or date), for example:
- Variables - $number1 or $number2.
- Fixed number values.
- Returned values from different functions - DATE() or SUM().
Output:
The function returns a boolean value (True or False).
Examples:
Table 36: Inputs/Outputs
| Input | Output |
| LESS_THAN_EQUAL(DATE(2022,01,05), DATE(2022,01,05)) | The function returns a boolean value: True |
| GREATER_THAN_EQUAL(SUM($num1, $num2, $num3), $number) For example: $number = 300 $num1 = 50 $num2 = 100 $num3 = 100 | The function returns a boolean value: True |
LN()
The following sections describe the LN(value) function.
General Description
This function returns the natural logarithm of the value.
Input and Output
Input:
The function receives on number type input parameter, for example:
- Variables - $number1 or $number2.
- Fixed number value.
- Returned values from different functions - DATE() or SUM().
Output:
The function returns a number.
Examples:
Table 37: Inputs/Outputs
| Input | Output |
| LN(1) | The function returns the natural logarithm - 0 |
LOOKUP()
The following sections describe the LOOKUP(operator, search_key, search_array, result_array) function.
General Description
This function looks for a value in a search array and returns the value of the corresponding item (in the same position/index) of a result array.
Input and Output
Input:
The function receives four input parameters:
- logical_expression that is comprised of:
- Comparison operators:
- =
- !=
- >
- <
- >=
- <=
- Comparison operators:
- search_key (string, number, boolean):
- Array items - for example: $children[0].firstName, $isMarried[1].
- Variables - for example: $number, $word, $booleanValue.
- Fixed values - for example: 8, "word", True.
- Other functions, for examples: DATE_FORMAT(), SUM(), ALL().
- search_array and result_array - a string, number, or boolean Array, for example:
- $children[*].firstName.
- $isMarried[*].
- TO_ARRAY().
Output:
The function returns an item (string, number, boolean) from the result_array.
Examples:
Table 38: Inputs/Outputs
| Input | Output |
| LOOKUP("=", "Dana", $firstName[*], $isMarried[*]) For example: $firstName[0] = "Dennis" $firstName[1] = "Dana" $isMarried[0] = False $isMarried[1] = True | The function checks if the firstName Array contains the firstName "Dana" and if so returns the item in the corresponding position/index from the isMarried Array, for example: True |
| LOOKUP("=","b", TO_ARRAY("a","b","c"),TO_ARRAY(True, 7,"3")) | The function checks if the search array that was created using the TO_ARRAY() function contains the string "b" and if so returns the item in the corresponding position/index from the result array that was created using the TO_ARRAY() function, for example: 7 |
LOOKUP_ARRAY()
The following sections describe the LOOKUP(operator, search_key, search_array, result_array) function.
General Description
This function looks for a value in a search array and returns multiple values of the corresponding item (in the same position/index) of a result array.
Input and Output
Input:
The function receives four input parameters:
- logical_expression that is comprised of:
- Comparison operators:
- =
- !=
- >
- <
- >=
- <=
- Comparison operators:
- search_key (string, number, boolean):
- Array items - for example: $children[0].firstName, $isMarried[1].
- Variables - for example: $number, $word, $booleanValue.
- Fixed values - for example: 8, "word", True.
- Other functions - for examples: DATE_FORMAT(), SUM(), ALL().
- search_array and result_array - a string, number, or boolean Array, for example:
- $children[*].firstName.
- $isMarried[*].
- TO_ARRAY().
Output:
The function returns multiple values.
- Because the function returns an array of values, it must be wrapped in a function such as JOIN() or CONCAT(), and in addition, all its variables and fixed values must be string type.
- For additional information about the JOIN() function, click here.
- For additional information about the Contact() function, click here.
Examples:
Table 39: Inputs/Outputs
| Input | Output |
| JOIN(LOOKUP_ARRAY("=", "Dana", $person[*].firstName, $isMarried[*]), ",") For example: $person[0].firstName = "Dana" $person[0].firstName = "Dana" $isMarried[0] = "False" $isMarried[1] = "True" | The function checks if the firstName Array contains the firstName "Dana" and if so returns the items in the corresponding positions/indexes from the isMarried Array, for example: "False", "True" |
| JOIN(LOOKUP_ARRAY("=","b", TO_ARRAY("a","b","c"),TO_ARRAY("True","7","3")), ",") | The function checks if the search array that was created using the TO_ARRAY() function contains the string "b" and if so returns the items in the corresponding positions/indexes from the result array that was created using the TO_ARRAY() function, for example: 7 |
LOWER()
The following sections describe the LOWER(text) function.
General Description
This function converts the characters of the input text from uppercase to lowercase.
Input and Output
Input:
The function receives one string type input parameter, for example:
- Array items - $kids[0].firstName or $color[1].
- Variables - $text1, $text2.
- Fixed values.
- Returned values from different functions - JOIN() or DATE_FORMAT().
Output:
The function returns a string.
Examples:
Table 40: Inputs/Outputs
| Input | Output |
| Lower(DATE_FORMAT(DATE(2202,05,01), "yyyy-MMM-dd")) | The function returns the text: "2202-may-01" |
| Lower($kids[1].firstName) For example: $kids[1].firstName = "DANA" | The function returns the text: "dana" |
LOWER_ARRAY()
The following sections describe the LOWER_ARRAY(array) function.
General Description
This function converts characters of an input Array from uppercase to lowercase.
Input and Output
Input:
The function receives one input parameter, for example:
- String type Array - $kids[*].firstName or $colors[*].
- Returned Array from the TO_ARRAY() function.
Output:
The function returns multiple strings.
- Because the function returns an array of values, it must be wrapped in a function such as JOIN() or CONCAT(), and in addition, all its variables and fixed values must be string type.
- For additional information about the JOIN() function, click here.
- For additional information about the Contact() function, click here.
Examples:
Table 41: Inputs/Outputs
| Input | Output |
| JOIN(LOWER_ARRAY($kids[*].firstName), ",") For example: $kids[0].firstName = "DENNIS" $kids[1].firstName = "DEE" | The function returns: "dennis",dee" |
| JOIN(LOWER_ARRAY(TO_ARRAY("RONNY","DANA")), ",") | The function returns: "ronny","dana" |
MAX()
The following sections describe the MAX(items) function.
General Description
This function returns the maximum value from a list of numbers, ignoring empty values.
Input and Output
Input:
The function receives a number Array or multiple number variables/values as input parameters (items), for example:
- Array items - $kids[0].age or $age[1].
- Variables - $num1 or $num2.
- Fixed values.
- Returned values from different functions - SUM() or MIM().
Output:
The function returns a number.
Examples:
Table 42: Inputs/Outputs
| Input | Output |
| MAX($num1,$num2,$num3) | The function returns the variable with the biggest value |
| MAX(SUM($num1,$num2),90) | The function returns the biggest value, either the value returned from the SUM() function or the fixed number value |
MIN()
The following sections describe the MIN(items) function.
General Description
This function returns the minimum value from a list of numbers, ignoring empty values.
Input and Output
Input:
The function receives a number Array or multiple number variables/values as input parameters (items), for example:
- Array items - $kids[0].age or $age[1].
- Variables - $num1, $num2.
- Fixed values.
- Returned values from different functions - SUM() or MIM().
Output:
The function returns a number.
Examples:
Table 43: Inputs/Outputs
| Input | Output |
| MIN($num1,$num2,$num3) | The function returns the variable with the lowest value |
| MIN(SUM($num1,$num2),90) | The function returns the lowest value, either the value returned from the SUM() function or the fixed number value |
MONTH()
The following sections describe the MONTH(date) function.
General Description
This function returns the month of a specific date according to a format.
Input and Output
Input:
The function receives a date parameter returned from a different function, for example:
- MONTH(TO_DATE($customer[0].dateBirth, "yyyy-dd-MM")).
- MONTH(DATE(1985/05/01)).
Output:
The function returns a number.
Examples:
Table 44: Inputs/Outputs
| Input | Output |
| MONTH(TO_DATE($date, "yyyy-MM-dd")) For example: $date = 1985-01-05 | The function returns a day according to the format: 01 |
| MONTH(TO_DATE($date, "yyyy-dd-MM"")) For example: $date = 1985-01-05 | The function returns a day according to the format: 05 |
| MONTH(DATE(1985,03,12)) | The function returns a day according to the format of the DATE() function: 03 |
MULTIPLY()
The following sections describe the MULTIPLY(value1, value2) function.
General Description
This function returns the multiplication product of two numbers.
Input and Output
Input:
The function receives two number type input parameters:
- Array items - for example: $children[0].age or $salary[1].
- Variables - for example: $Age or $spouseAge.
- Fixed values.
- A returned value from a different function - for example: SUM() or MIM().
Output:
The function returns a number.
Examples:
Table 45: Inputs/Outputs
| Input | Output |
| MULTIPLY($age, 5) | The function returns the multiplication product of the age variable and the number 5 |
| MULTIPLY(SUM($num1, $num2), MAX($salary, $spouseSalary)) | The function returns the multiplication product of the returned values from the SUM() and MAX() functions |
NOT()
The following sections describe the NOT(logical_expression) function.
General Description
This function returns the opposite value of a boolean input.
Input and Output
Input:
The function receives one boolean type input parameter:
- Array items - for example: $personalDetails[0].isMarried or $status[1].
- Variables - for example: $houseOwner or $isMarried.
- Fixed values.
- A returned value from a different function - for example: ALL() or ANY().
Output:
The function returns a boolean value (True or False).
Examples:
Table 46: Inputs/Outputs
| Input | Output |
| NOT($isMarried) For example: $isMarried = True | The function returns the opposite value of the boolean input, for example: False |
NOT_EQUAL()
The following sections describe the NOT_EQUAL(value1, value2) function.
General Description
This function checks if two values are not equal.
Input and Output
Input:
The function receives two input parameters from any type (number, string, boolean, date):
- Array items - for example: $children[1] or $children[0].age
- Variables - for example: $word, $number1, $isMarried.
- Fixed values - for example: "True", True, 8.
- Returned values from different functions - DATE(), SUM(), ANY().
Output:
The function returns a boolean value (True or False).
Examples:
Table 47: Inputs/Outputs
| Input | Output |
| NOT_EQUAL(DATE(2022,01,05), DATE(2022,06,07)) | The function returns a boolean value: True |
| EQUAL($children[0].FirstName, "Dana") For example: $children[0].firstName = "Dana" | The function returns a boolean value: False |
| EQUAL($number, 8) For example: $number = 8 | The function returns a boolean value: False |
OR()
The following sections describe the OR(logical_expression) function.
General Description
This function returns False if any of the provided arguments are logically True, and False if all the provided arguments are logically False.
Input and Output
Input:
The function receives one boolean type input parameter:
- Array items - for example: $personalDetails[0].isMarried or $status[1].
- Variables - for example: $houseOwner or $isMarried.
- Fixed values.
- A returned value from a different function - for example: ALL() or ANY().
Output:
The function returns a boolean value (True or False).
Examples:
Table 48: Inputs/Outputs
| Input | Output |
| OR($isMarried, $hasChildren) For example: $isMarried = True $hasChidren = False | The function returns False |
PAD()
The following sections describe the PAD(str, output_length, padding_element, padding format) function.
General Description
This function adds padding to a string up to the output length.
Input and Output
Input:
The function receives four input parameters:
- str (string):
- Arrays items - for example: $children[1].name or $names[0].
- String variables - for example: $word1 or $word2.
- Fixed values.
- Returned values from different functions such as TO_TEXT()
- output_length (number):
- Variables - $number1 or $isMarried.
- Fixed values.
- padding_element (string):
- Variables - for example: $word1 or $word2.
- Fixed values - for example: "*" or "/".
- padding_element (number) - 0 (right padding), 1 (left padding).
Output:
The function returns a string.
Examples:
Table 50: Inputs/Outputs
| Input | Output |
| PAD("12345", 10, "*", 0) | The function returns a string: "12345*****" |
| PAD($children[0].FirstName, 10, "*", 1) For example: $children[0].firstName = "Dana" | The function returns a string: "******Dana" |
PAD_ARRAY()
The following sections describe the PAD_ARRAY(array, output_length, padding_element, padding format) function.
General Description
This function adds padding to all string values Array items up to their output length.
Input and Output
Input:
The function receives four input parameters:
- array (string), for example:
- $children[*].name.
- $names[*].
- Returned Array for the TO_ARRY() function.
- output_length (number):
- Variables - $number1 or $isMarried.
- Fixed values.
- padding_element (string):
- Variables - for example: $word1 or $word2.
- Fixed values - for example: "*" or "/".
- padding_element (number) - 0 (right padding), 1 (left padding).
Output:
The function returns multiple strings.
- Because the function returns an array of values, it must be wrapped in a function such as JOIN() or CONCAT(), and in addition, all its variables and fixed values must be string type.
- For additional information about the JOIN() function, click here.
- For additional information about the Contact() function, click here.
Examples:
Table 51: Inputs/Outputs
| Input | Output |
| JOIN(PAD_ARRAY(TO_ARRAY("12", "10", "900"), 3, "*", 0), ",") | The function returns: "12*", "10*" ,"900" |
| JOIN(PAD($FirstName[*], 6, "*", 1), ",") For example: $firstName[0] = "Dana" $firstName[1] = "Ronny" $firstName[2] = "Dee" | The function returns: "**Dana", "*Ronny" ,"***Dee" |
POSITION()
The following sections describe the POSITION(search_text, text_to_search, case_sensitive, starting_at_position) function.
General Description
This function returns the position at which a string/array is first found within text.
Input and Output
Input:
The function receives five input parameters:
- search_text, text_to_search (string), for example:
- Array items - $kids[0].firstName or names[1].
- Variables - $word1 or $word2.
- Fixed values.
- Returned values from different functions such as TO_TEXT()or JOIN().
- case_sensitive (boolean) - True or False.
- starting_at_position (number).
Output:
The function returns a number as a string.
Examples:
Table 52: Inputs/Outputs
| Input | Output |
| POSITION("DANA", "dana", True, 0) | The function returns "-1" because it is case sensitive |
| POSITION("DANA", "dana", False, 7) | The function returns "-1" because the search starts at the 7th character |
| IF(POSITION($word,"yes" , False, 0) = "1", True, False)) $word = "Yes" | The function returns true because case sensitive is false |
POWER()
The following sections describe the POWER(base, exponent) function.
General Description
This function returns an exponential number (raised to a power).
Input and Output
Input:
The function receives two number type input parameters (base and exponent):
- Array items - for example- $children[0].age or $salary[1].
- Variables - for example - $Age or $spouseAge.
- Fixed values.
- A returned value from a different function - for example: SUM() or MIM().
Output:
The function returns a number.
Examples:
Table 53: Inputs/Outputs
| Input | Output |
| POWER($age,2) | The function returns the value of the age variable to the power of 2 |
PROPER()
The following sections describe the PROPER(base, exponent) function.
General Description
This function capitalizes the first character of a word in a specified string and converts the following characters to lowercase.
Input and Output
Input:
The function receives one string type input parameter (text):
- Array items - for example: $children[0].name or $name[1].
- Variables - for example: $word1 or $word2.
- Fixed values.
- A returned value from a different function - for example: TO_TEXT().
Output:
The function returns a number.
Examples:
Table 54: Inputs/Outputs
| Input | Output |
| PROPER("dANA") | The function returns the value "Dana" |
RAND_BETWEEN()
The following sections describe the RAND_BETWEEN(low, high) function.
General Description
This function returns a uniformly random integer between two values, inclusive of those values.
Input and Output
Input:
The function receives two number type input parameters (low, high):
- Array items - for example: $children[0].age or $age[1].
- Variables - for example: $num1 or $num2.
- Fixed values.
- A returned value from a different function - for example: SUM().
Output:
The function returns a number.
Examples:
Table 55: Inputs/Outputs
| Input | Output |
| RAND_BETWEEN(1,5) | The function returns a random number between 1 and 5 |
REGEX_EXTRACT()
The following sections describe the REGEX_EXTRACT(text, regular_expression) function.
General Description
This function extracts matching substrings according to a regular expression.
Input and Output
Input:
The function receives two string input parameters:
- text :
- Array items - for example: $children[1].name or $names[0].
- Variables - for example: $word1 or $word2.
- Fixed values.
- Returned values from different functions such as TO_TEXT().
- regular expression - tokens of regular expressions such as:
- "\d+"
- "\d*"
- "\w+"
- "\s"
Output:
The function returns a string.
Examples:
Table 56: Inputs/Outputs
| Input | Output |
| REGEX_EXTRACT("James Bond 007 not 008", "\d+" ) | The function extracts and returns the substring "007" |
REGEX_MATCH()
The following sections describe the REGEX_MATCH(text, regular_expression) function.
General Description
This function checks whether a portion of text matches a regular expression.
Input and Output
Input:
The function receives two string input parameters:
- text :
- Array items - for example: $children[1].name or $names[0].
- Variables - for example: $word1 or $word2.
- Fixed values.
- Returned values from different functions such as TO_TEXT().
- regular expression - tokens of regular expressions such as:
- "\d+"
- "\d*"
- "\w+"
- "\s"
Output:
The function returns a boolean value (True or False).
Examples:
Table 57: Inputs/Outputs
| Input | Output |
| REGEX_MATCH("007", "\d+" ) | The function returns True |
REGEX_REPLACE()
The following sections describe the REGEX_REPLACE(text, regular_expression, replacement_text) function.
General Description
This function replaces matching substrings according to a regular expression.
Input and Output
Input:
The function receives three string input parameters:
- text and replacement_text:
- Array items - for example: $children[1].name or $names[0].
- Variables - for example: $word1 or $word2.
- Fixed values.
- Returned values from different functions such as TO_TEXT().
- regular expression - tokens of regular expressions such as:
- "\d+"
- "\d*"
- "\w+"
- "\s"
Output:
The function returns a string.
Examples:
Table 58: Inputs/Outputs
| Input | Output |
| REGEX_REPLACE("James Bond 007", "\d+", "008") | The function replaces the substring "007" with "008" and returns the result: "James Bond 008" |
REMOVE_EMPTY()
The following sections describe the REMOVE_EMPTY(array) function.
General Description
This function removes empty strings and null values from an Array.
Input and Output
Input:
The function receives an Array or multiple variables/values of any type as input parameters (array):
- Array or Array items - for example: $children[*].age, $salary[*], $children[0].age, $salary[1].
- Variables - for example: $Age, $isMarried, $word.
- Fixed values - for example: 8, True, "True".
- A returned value from a different function - for example: DATE(), TO_TEXT(), MIM().
Output:
The function returns multiple strings.
- Because the function returns an array of values, it must be wrapped in a function such as JOIN() or CONCAT(), and in addition, all its variables and fixed values must be string type.
- For additional information about the JOIN() function, click here.
- For additional information about the Contact() function, click here.
Examples:
Table 59: Inputs/Outputs
| Input | Output |
| JOIN(REMOVE_EMPTY($names[*]), ",") For example: details[0].name = "Ronny" details[1].name = details[2].name = "Dana" | The function removes empty strings from the names Array and returns the Array, for example: "Ronny","Dana" |
REPLACE()
The following sections describe the REPLACE(text, position, length, replacement_text) function.
General Description
This function replaces a portion of a text with a different text.
Input and Output
Input:
The function receives four input parameters:
- text and replacement_text (string), for example:
- Array items - $kids[0].firstName or names[1].
- Variables - $word1 or $word2.
- Fixed values.
- Returned values from different functions such as TO_TEXT().
- position and length (number), for example:
- Variables - $num1 or $num2.
- Fixed values.
Output:
The function returns a string.
Examples:
Table 60: Inputs/Outputs
| Input | Output |
| REPLACE("hi there", 4, 3, "B") | The function replaces the text starting from the 4th character until the 6th, for example: "hi Bre" |
ROUND()
The following sections describe the ROUND(value, place) function.
General Description
This function rounds a number to a certain number of decimal places according to standard rules.
Input and Output
Input:
The function receives two number type input parameters - value and place:
- Array items - $details[0].age or age[1].
- Variables - $num1 or $num2.
- Fixed values.
Output:
The function returns a number
Examples:
Table 61: Inputs/Outputs
| Input | Output |
| ROUND(4.55555,2) | The function returns the number 4.56 |
| ROUND(4.5) | The function returns the number 5 |
SUBSTITUTE()
The following sections describe the SUBSTITUTE(search_text, text_to_search, replace_with, case_sensitive, occurrence_number) function.
General Description
This function replaces existing text with new text in a string.
Input and Output
Input:
The function receives five input parameters:
- search_text, text_to_search, replace_with(string), for example:
- Array items - $kids[0].firstName or names[1].
- Variables - $word1 or$word2.
- Fixed values.
- Returned values from different functions such as TO_TEXT()or JOIN().
- case_sensitive (boolean) - True or False.
- occurrence_number (number).
Output:
The function returns a string.
Examples:
Table 62: Inputs/Outputs
| Input | Output |
| SUBSTITUTE($maritalStatus, "single", "Married", False, 1) For example: $maritalStatus = "single" |
|
SUBSTITUTE_ARRAY()
The following sections describe the SUBSTITUTE_ARRAY(search_text, text_to_search, replace_with, case_sensitive, occurrence_number) function.
General Description
This function replaces existing text with new text in a string for all items in an array.
Input and Output
Input:
The function receives five input parameters:
- search_text a string type Array, for example:
- $kids[*].firstName.
- names[*].
- text_to_search, replace_with(string), for example:
- Array items - $kids[0].firstName or names[1].
- Variables - $word1 or $word2.
- Fixed values.
- Returned values from different functions such as TO_TEXT() or JOIN().
- case_sensitive (boolean) - True or False.
- occurrence_number (number).
Output:
The function returns multiple strings.
- Because the function returns an array of values, it must be wrapped in a function such as JOIN() or CONCAT(), and in addition, all its variables and fixed values must be string type.
- For additional information about the JOIN() function, click here.
- For additional information about the Contact() function, click here.
Examples:
Table 63: Inputs/Outputs
| Input | Output |
| JOIN(SUBSTITUTE_ARRAY($maritalStatus[*], "single", "Married", False, 1), ",") |
|
SPLIT()
The following sections describe the SPLIT(str_to_split, split_by) function.
General Description
This function splits one string into an array of strings.
Input and Output
Input:
The function receives two string type input parameters, str_to_split and split_by:
- Array items - $kids[0].firstName or names[1].
- Variables - $word1 or $word2.
- Fixed values.
- Returned values from different functions such as TO_TEXT().
Output:
The function returns multiple strings.
Examples:
Table 64: Inputs/Outputs
| Input | Output |
| JOIN(SPLIT($emailAddress, "@"), ",") For example: $emailAddress = "dana@gmail.com" | The function splits the string inside the emailAddress variable, for example: dana, gmail.com |
SQRT()
The following sections describe the SQRT(value1) function.
General Description
This function returns the square root of a positive number.
Input and Output
Input:
The function receives one number type input parameter:
- Array items - for example: $children[0].age or $salary[1].
- Variables - for example: $Age or $spouseAge.
- Fixed values.
- A returned value from a different function - for example: SUM() or MIM().
Output:
The function returns a number.
Examples:
Table 65: Inputs/Outputs
| Input | Output |
| SQRT($age) | The function returns the square root of the variable age value |
| SQRT(SUM($num1,$num2)) | The function returns the square root of the value returned from the SUM() function |
SUBSTRING()
The following sections describe the SUBSTRING(text, start_index, length) function.
General Description
This function returns a segment of a string. Beginning with the start index and up to a specific length.
Input and Output
Input:
The function receives three input parameters:
- substring (string):
- Array items - for example: $children[0].age or $salary[1].
- Variables - for example: $Age or $spouseAge.
- Fixed values.
- A returned value from a different function - for example: TO_TEXT().
- start_index and length (number):
- Variables - for example: $num1, $num2.
- Fixed values.
Output:
The function returns a string.
Examples:
Table 66: Inputs/Outputs
| Input | Output |
| SUBSTRING("Dana", 3, 3) | The function returns the substring "na" |
SUBTRACT()
The following sections describe the SUBTRACT(value1, value2) function.
General Description
This function returns the difference (subtraction result) of two numbers.
Input and Output
Input:
The function receives two input number type parameters:
- Array items - for example: $children[0].age or $salary[1].
- Variables - for example: $Age or $spouseAge.
- Fixed values.
- A returned value from a different function - for example: SUM() or MIM().
Output:
The function returns a number.
Examples:
Table 67: Inputs/Outputs
| Input | Output |
| SUBTRACT($age, 5) | The function returns the difference between the age variable and the number 5 |
| SUBTRACT(-10, 100) | The function returns the difference between the two fixed numbers, for example: -110 |
SUM()
The following sections describe the SUM(items) function.
General Description
This function returns the sum of multiple numbers. Equivalent to the `+` operator.
Input and Output
Input:
The function receives a number Array or multiple number variables/values as input parameters (items):
- Array items - for example: $children[0].age or $salary[1].
- Variables - for example: $Age or $spouseAge.
- Fixed values.
- A returned value from a different function - for example: MAX() or MIM().
Output:
The function returns a number.
Examples:
Table 68: Inputs/Outputs
| Input | Output |
| SUM($age, 5) | The function returns the sum value of the age variable and the number 5 |
| SUM(-10, 100) | The function returns the sum value of the two fixed numbers, for example: 90 |
SUM_IF()
The following sections describe the SUM_IF(operator, criterion, items) function.
General Description
This function returns a conditional sum across a range.
Input and Output
Input:
The function receives three input parameters:
- operator (string):
- =
- !=
- >
- <
- >=
- <=
- criterion (number):
- Array items, for example: $children[0].firstName or $isMarried[1].
- Number variables, for example: $num1 or $num2.
- Fixed values.
- Other functions, for examples: MIN(), SUM(), MAX(), UNIQUE().
- items - a number Array or multiple number variables/values as input parameters (items):
- Array items - for example: $children[0].age or $salary[1].
- Variables - for example: $Age or $spouseAge.
- Fixed values.
- Other functions, for examples: MIN(), SUM(), MAX(), UNIQUE().
Output:
The function returns a number.
Examples:
Table 69: Inputs/Outputs
| Input | Output |
| SUM_IF(">=", 1000, $bills[*] ) | The function returns the sum of all the bills Array values that are equal to or greater than 1000 |
SWITCH()
The following sections describe the SWITCH(checked_value, case, result, default) function.
General Description
This function checks a value against cases and returns a matching single value result.
Input and Output
Input:
The function receives four input parameters:
- checked_value (string, number, boolean):
- Array items - for example: $children[0].firstName or $isMarried[1].
- Variables - for example: $num1, $word, $isMarried.
- Fixed values - for example: 8, True, "True".
- Other functions - for examples: MIN(), SUM(), MAX(), UNIQUE().
- case - (string, number, boolean):
- Array or Array items - for example: $children[*].firstName, $isMarried[*], $children[0].firstName, $isMarried[1]
- Variables - for example: $num1, $word, $isMarried.
- Fixed values - for example: 8, True, "True".
- Other functions - for examples: TO_ARRAY(), SUM(), MAX(), UNIQUE().
- result and default (string, number, boolean):
- Array items - for example: $children[0].firstName, $isMarried[1].
- Variables - for example: $num1, $word, $isMarried.
- Fixed values - for example: 8, True, "True".
- Other functions - for examples: MIN(), SUM(), MAX().
Output:
The function returns a single value (string, number, or boolean).
Examples:
Table 70: Inputs/Outputs
| Input | Output |
| SWITCH($clientOccupation, "singer", 500, "author", 300, 200) For example: $clientOccupation = "singer" | The function checks the value of the clientOccupation variable against all the cases and returns a value, for example: 500 |
SWITCH_ARRAY()
The following sections describe the SWITCH_ARRAY(checked_value, case, array_result, default) function.
General Description
This function checks a value against cases and returns a matching array result.
Input and Output
Input:
The function receives four input parameters:
- checked_value (string, number, boolean):
- Array items - for example: $children[0].firstName or $isMarried[1].
- Variables - for example: $num1, $word, $isMarried.
- Fixed values - for example: 8, True, "True".
- Other functions - for examples: MIN(), SUM(), MAX(), UNIQUE().
- case, array_result, and default (string, number, boolean):
- Array or Array items, for example: $children[*].firstName, $isMarried[*], $children[0].firstName, $isMarried[1]
- Variables - for example: $num1, $word, $isMarried.
- Fixed values - for example: 8, True, "True".
- Other functions - for examples: TO_ARRAY(), SUM(), MAX(), UNIQUE().
Output:
The function returns multiple values (string, number, or boolean)
- Because the function returns an array of values, it must be wrapped in a function such as JOIN() or CONCAT(), and in addition, all its variables and fixed values must be string type.
- For additional information about the JOIN() function, click here.
- For additional information about the Contact() function, click here.
Examples:
Table 71: Inputs/Outputs
| Input | Output |
| JOIN(SWITCH_ARRAY($clientOccupation, TO_ARRAY("singer", "dancer"), $singerArray[*], "author", $authorsArray[*], $defaultArray[*]), ",") For example: $client.occupation = "singer" | The function checks the value of the clientOccupation variable against the cases returned from the TO_ARRAY() function and returns an Array according to the result |
TO_ARRAY()
The following sections describe the TO_ARRAY(str) function.
General Description
This function converts a provided set of values into an Array.
Input and Output
Input:
The function receives an Array or multiple variables/values of any type as input parameters (str):
- Array or Array items - for example: $kids[*].birthDay, $birthdays[*], $kids[0].birthDay, $birthdays[1].
- Variables - for example: $num, $word, $isMarried.
- Fixed values - for example: "2202/05/01", True, 8.
- Returned values from different functions, such as: DATE(), TO_TEXT(), TO_NUM().
Output:
The function returns multiple strings.
- Because the function returns an array of values, it must be wrapped in a function such as JOIN() or CONCAT(), and in addition, all its variables and fixed values must be string type.
- For additional information about the JOIN() function, click here.
- For additional information about the Contact() function, click here.
Examples:
Table 72: Inputs/Outputs
| Input | Output |
| JOIN(TO_ARRAY(3, "Dana", "True", "5", "12/3/1985" ), ",") | The function returns a new Array with the provided values |
TO_DATE()
The following sections describe the TO_DATE(string_date, format) function.
General Description
This function converts a string date with a predefined format to a date type.
Input and Output
Input:
The function receives two input parameters:
- string_date (string):
- Array items - for example: $kids[0].birthDay or $birthdays[1].
- Variables - for example: $birthDay.
- fixed values - for example: "2202/05/01".
- format - comprised of a month, day, and year. For example:
- "d/M/y" or "d-M-y" - (1/5/85 or 1-5-85).
- "dd/MM/yy" or "dd-MM-yy" (01/05/85 or 01-05-85).
- "ddd/MMM/yyyy" or "ddd-MMM-yyyy" (Mon/Feb/1985 or Mon-Feb-1985).
- "dddd/MMMM/yyyy" or "dddd-MMMM-yyyy" (Monday/February/1985 or Monday/February/1985).
Output:
The function returns a date.
Examples:
Table 73: Inputs/Outputs
| Input | Output |
| DATE_FORMAT(TO_DATE("1985-5-1", "yyyy-MM-dd"),"yyyy-MM-dd") | The function returns a date in the following format: 1985-05-01 |
TO_NUM()
The following sections describe the TO_NUM(str, separator_style) function.
General Description
This function converts a string to a number.
Input and Output
Input:
The function receives two string type input parameters:
- str:
- Array items - for example: $kids[0].birthDay or $birthdays[1].
- Variables - for example: $word1.
- Fixed values - for example: "1234".
- Returned values from different functions, such as TO_TEXT().
- separator_style - an optional parameter that determines the separator style between digits, for example:
- Fixed values - for example: "us" (default) or "de".
- Variables - for example: $separatorType.
Output:
The function returns a number.
Examples:
Table 74: Inputs/Outputs
| Input | Output |
| TO_NUM("1234") | The function returns a new number: 1234 |
| TO_NUM("1,234.15") | The function returns a new number: 1234.15 |
| TO_NUM("1.234.15","de") | The function returns a new number: 1234.15 |
TO_TEXT()
The following sections describe the TO_TEXT(value) function.
General Description
This function converts a value to a string.
Input and Output
Input:
The function receives one input parameter - value (string, number, boolean):
- Array items - for example: $kids[0].birthDay or $isMarried[1].
- Variables - for example: $word1, $num1, $isMarried.
- Fixed values - for example: "1234", True, 8.
- Returned values from different functions, such as SUM(), ANY(), MAX().
Output:
The function returns a string value.
Examples:
Table 75: Inputs/Outputs
| Input | Output |
| TO_TEXT(True) | The function returns a new string: "True" |
TRIM()
The following sections describe the TRIM(text, padding_element_to_trim) function.
General Description
This function removes leading and tailing padding elements in a string.
Input and Output
Input:
The function receives two string type input parameters (text, padding_element_to_trim):
- Array items - for example: $children[0].name, $name[1].
- Variables - for example: $word.
- Fixed values.
- A returned value from a different function - for example: TO_TEXT().
Output:
The function returns a string.
Examples:
Table 76: Inputs/Outputs
| Input | Output |
| TRIM("***Dana***","*") | The function returns a trimmed string: "Dana" |
TYPE()
The following sections describe the TYPE(value) function.
General Description
This function returns the type of value/variable that was entered into the function.
Input and Output
Input:
The function receives one input parameter from any type (string, number, boolean, date):
- Array items - for example: $children[0].age or $salary[1].
- Variables - for example: $Age or $spouseAge.
- Fixed values - for example: True, "True", 8.
- A returned value from a different function - for example: TO_TEXT(), MIN(), or DATE().
Output:
The function returns a string.
Examples:
Table 77: Inputs/Outputs
| Input | Output |
| TYPE($isMarried) For example: $isMarried = True | The function checks the type of the variable and returns a string indicating its type, for example: boolean |
| TYPE($isMarried) For example: $isMarried = "True" | The function checks the type of the variable and returns a string indicating its type, for example: string |
| TYPE(date(2022,05,01)) | The function checks the type of the return value from the DATE() function and returns a string indicating its type, for example: date |
UNIQUE()
The following sections describe the UNIQUE(array) function.
General Description
This function returns the unique items of an Array.
Input and Output
Input:
The function receives one input parameter, an Array (string, boolean, number):
- Array - for example: $children[*], $children[*].firstName, $isMarried[*].
- Array items - for example: $children[0], $children[1].firstName, $isMarried[2].
- Variables - for example: $word1, $num1, isMarried.
- Fixed values - for example: "1234", True, 8.
- An Array returned from the TO_ARRAY() function.
Output:
The function returns multiple string values.
- Because the function returns an array of values, it must be wrapped in a function such as JOIN() or CONCAT(), and in addition, all its variables and fixed values must be string type.
- For additional information about the JOIN() function, click here.
- For additional information about the Contact() function, click here.
Examples:
Table 78: Inputs/Outputs
| Input | Output |
| JOIN(UNIQUE($colors[*]), ",") For example: $colors[0] = "blue" $colors[1] = "blue" $colors[2] = "yellow" $colors[3] = "white" | The function checks the colors Array for unique values and returns them, for example: "blue","yellow","white" |
UPPER()
The following sections describe the UPPER(text) function.
General Description
This function converts the characters of the input text from lowercase to uppercase.
Input and Output
Input:
The function receives one string type input parameter, for example:
- Array items - $kids[0].firstName and $color[1].
- Variables - $text1, $text2.
- Fixed values.
- Returned values from different functions - JOIN() or DATE_FORMAT().
Output:
The function returns a string.
Examples:
Table 79: Inputs/Outputs
| Input | Output |
| UPPER(DATE_FORMAT(DATE(2202,05,01), "yyyy-MMM-dd")) | The function returns the text: 2202-MAY-01 |
| UPPER($kids[1].firstName) For example: $kids[1].firstName = "dana" | The function returns the text: "DANA" |
UPPER_ARRAY()
The following sections describe the UPPER_ARRAY(array) function.
General Description
This function converts characters of an input Array from lowercase to uppercase.
Input and Output
Input:
The function receives one input parameter, for example:
- String type Array - $kids[*].firstName and $colors[*].
- Returned Array from the TO_ARRAY() function.
Output:
The function returns multiple strings.
- Because the function returns an array of values, it must be wrapped in a function such as JOIN() or CONCAT(), and in addition, all its variables and fixed values must be string type.
- For additional information about the JOIN() function, click here.
- For additional information about the Contact() function, click here.
Examples:
Table 80: Inputs/Outputs
| Input | Output |
| JOIN(LOWER_ARRAY($kids[*].firstName), ",") For example: $kids[1].firstName = "dennis" $kids[1].firstName = "dee" | The function returns: "DENNIS",DEE" |
| JOIN(LOWER_ARRAY(TO_ARRAY("ronny","dana")), ",") | The function returns: "RONNY","DANA" |
VALUE()
The following sections describe the VALUE(reference_array, position) function.
General Description
This function returns a value from an Array according to the provided position.
Input and Output
Input:
The function receives two input parameters:
- reference_array (string, number, boolean):
- Array - for example: $kids[*].names or names[*].
- A returned Array from the TO_ARRAY() function.
- position (number):
- Variable.
- Fixed value.
Output:
The function returns a value (string, number, boolean).
Examples:
Table 81: Inputs/Outputs
| Input | Output |
| VALUE(fullName[*], 0) | The function returns the first fullName value from the Array |
WEEK_DAY()
The following sections describe the WEEK_DAY(date) function.
General Description
This function returns a number representing the day of the week of the date provided (Sunday=1).
Input and Output
Input:
The function receives one date type input parameter from date type functions such as:
- DATE()
- TO_DATE()
Output:
The function returns a number.
Examples:
Table 82: Inputs/Outputs
| Input | Output |
| WEEK_DAY(DATE(2022, 09, 28)) | The function returns the number 4 because the day is Wednesday |
| WEEK_DAY(DATE(2022,01,04)) | The function returns the number 3 because the day is Tuesday |
WEEK_NUM()
The following sections describe the WEEK_NUM(date, week_starts_on) function.
General Description
This function returns a number representing the week of the year of the date provided.
Input and Output
Input:
The function receives one date type input parameter from date type functions such as DATE() or TO_DATE() and an optional string type parameter which represents the index of the first day of the week:
- 0 - Sunday
- 1 - Monday
- 2 - Tuesday
- 3 - Wednesday
- 4 - Thursday
- 5 - Friday
- 6 - Saturday
Output:
The function returns a number.
Examples:
Table 83: Inputs/Outputs
| Input | Output |
| WEEK_NUM(DATE(2023, 11, 26), 0) | The function returns the number 48 because this is the 48th week of the year |
| WEEK_NUM(DATE(2021, 12, 31), 0) | The function returns the number 53 because this is the last week of the year |
YEAR()
The following sections describe the YEAR(date) function.
General Description
This function returns the year of a specific date according to a format.
Input and Output
Input:
The function receives a date parameter returned from a different function, for example:
- YEAR(TO_DATE($customer[0].dateBirth, "yyyy-dd-MM")).
- YEAR(DATE(1985/05/01)).
Output:
The function returns a number.
Examples:
Table 84: Inputs/Outputs
| Input | Output |
| YEAR(TO_DATE($date, "yyyy-MM-dd")) For example: $date = 1985-01-05 | The function returns a day according to the format: 1985 |
| YEAR(date(99, 6,7) | The function returns a day according to the format: 1999 |
Formatting Functions ()
The following sections describe the Formula Editor's formatting functions.
FORMAT_TIN()
The following sections describe the FORMAT_TIN(tin_to_format) function.
General Description
This function converts a 9-digit number to a Taxpayer Identification Number (TIN) format.
Input and Output
Input:
The function receives one string type input parameter:
- Array items - for example: $format[0].tin or $tin[0].
- Variables - for example: $variable1 or $variable2.
- Fixed values.
Output:
The function returns a TIN formatted string.
Examples:
Table 85: Inputs/Outputs
| Input | Output |
| FORMAT_TIN($tin[0]) For example: $format[0].TIN = 123123456 | The function converts the first value in the tin Array to a TIN format, for example: "123-12-3456" |
| FORMAT_TIN("123456789") | The function converts the fix string value to a TIN format, for example: "123-45-6789" |
| FORMAT_TIN($number) For example: $number = 123123456 | The function converts the value in the number variable the to a TIN format, for example: "123-12-3456" |
FORMAT_PRECISION()
The following sections describe the FORMAT_PRECISION(number_to_format, precision) function.
General Description
This function formats a number to a given precision.
Input and Output
Input:
The function receives two input parameters:
- number_to_format (string):
- Array items - for example: $salary[0].amount or $salary[0].
- Variables - for example: $variable1 or $variable2.
- Fixed values.
- A returned string from the TO_TEXT() function.
- precision (number):
- Array items - for example: $salary[0].amount or $salary[0].
- Variables - for example: $variable1 or $variable2.
- Fixed values.
- A returned number from the TO_NUM() function.
Output:
The function returns a precise number (string).
Examples:
Table 86: Inputs/Outputs
| Input | Output |
| FORMAT_PRECISION($salary[0], 2) For example: $salary[0] = 1231.678 | The function converts the first value in the salary Array to a precise number (string), for example: "1231.67" |
| FORMAT_PRECISION("1234.56789", TO_NUM("3")) | The function converts the fix string value to a precise number (string), for example: "1234.567" |
| FORMAT_PRECISION($number1, $number2) For example: $number1 = 123.123456 $number2 = 4 | The function converts the value in the number variable to a precise number (string), for example: "123.1234" |
| FORMAT_PRECISION(TO_TEXT(sum($num1,$num2,$num3)),2) For example: $num1 = 100 $num2 = 200.504 $num3 = 300 | The function converts the value returned from the TO_TEXT() function to a precise number (string), for example: "600.50" |
FORMAT_SSN()
The following sections describe the FORMAT_SSN(ssn_to_format) function.
General Description
This function converts a 9-digit number to a Social Security Number (SSN) format.
Input and Output
Input:
The function receives one string type input parameter:
- Array items - for example: $format[0].ssn or $ss[0].
- Variables - for example: $variable1 or $variable2.
- Fixed values.
Output:
The function returns an SSN formatted string.
Examples:
Table 87: Inputs/Outputs
| Input | Output |
| FORMAT_SSN($format[0]) For example: $format[0].ssn = 123123456 | The function converts the value in the format Array to an SSN format, for example: "123-12-3456" |
| FORMAT_SSN("123456789") | The function converts the fixed string value to an SSN format, for example: "123-45-6789" |
| FORMAT_SSN($number) For example: $number = 123123456 | The function converts the value in the number variable the to an SSN format, for example: "123-12-3456" |
FORMAT_THOUSANDS()
The following sections describe the FORMAT_THOUSANDS(number_to_format, separator_style) function.
General Description
This function formats a number by adding separators.
Input and Output
Input:
The function receives two parameters:
- number_to_format (string/number):
- Array items - for example: $salary[0].amount or $salary[0].
- Variables - for example: $variable1 or $variable2.
- Fixed values - for example: 10000 or "10000".
- A returned string from the TO_TEXT() function.
- separator_style (string) - an optional parameter that determines the separator style between digits:
- Fixed values - for example: "us" (default), "de".
- Variables - for example: $separatorType.
Output:
The function returns a number (string) separated by separators.
Examples:
Table 88: Inputs/Outputs
| Input | Output |
| FORMAT_THOUSANDS($salary[0]) For example: $salary[0] = 10000 | The function converts the value in the salary Array to a number(string) separated by commas, for example: "10,000" (US style) |
| FORMAT_THOUSANDS("32423003.13","de") | The function converts the fix string value to a number (string) separated by commas, for example: "32.423.003,13" (de style) |
| FORMAT_THOUSANDS(TO_TEXT(sum($num1,$num2))) For example: $num1 = 100000 $num2 = 500 | The function converts the value returned from the TO_TEXT() function to a number (string) separated by commas, for example: "100,500" (US style) |
FORMAT_CUSTOM()
The following sections describe the FORMAT_CUSTOM(text, format_pattern) function.
General Description
This function converts and formats text according to a specified pattern.
Input and Output
Input:
The function receives two string type input parameters:
- text:
- Array items - for example: $format[0].ssn or $ss[0].
- Variables - for example: $variable1 or $variable2.
- Fixed values.
- format_pattern - the desired formatting pattern comprised of a pound sign (#) and separators.
Output:
The function returns a custom formatted string.
Examples:
Table 89: Inputs/Outputs
| Input | Output |
| FORMAT_CUSTOM("Dana", "#-#-#-#") | The function returns a custom formatted string, for example: "D-a-n-a" |
| FORMAT_CUSTOM("123456", "#/#/#/###") | The function returns a custom formatted string, for example: "1/2/3/456" |
Use Case Examples
The following sections describe a few use case examples of the Formula Editor feature.
Using a Function within a Function
We want the ALL() function to check if a value that is being returned from the MIN() function is lower than the value of a specific variable, and to return a boolean value, True or False. Figure 15 describes a data structure that contains four string type variables (1):
- num1
- num2
- num3
- num4
The data structure also contains a boolean type variable, result (2), that will contain the ALL() function returned value.
Figure 15: Data Structure
To use the formula editor, perform the following steps (see Figure 16 to Figure 19):
Figure 16: Formula Option
- Click the result variable (1).
- Click the Value dropdown (2).
- Click Formula (3).
Result:
The Edit Formula button (4) appears:
Figure 17: Edit Formula
- Click the Edit Formula button (4).
Result:
The Formula Editor window appears:
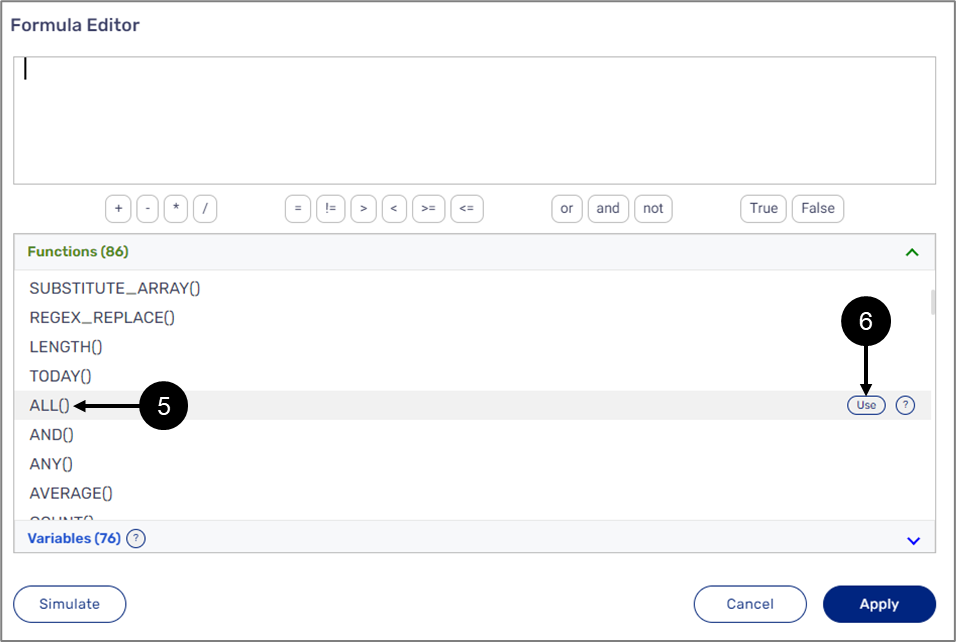
Figure 18: Adding the ALL() Function
- Locate the ALL() function (5).
- Double click it or click the Use button (6).
Result:
The function is added:
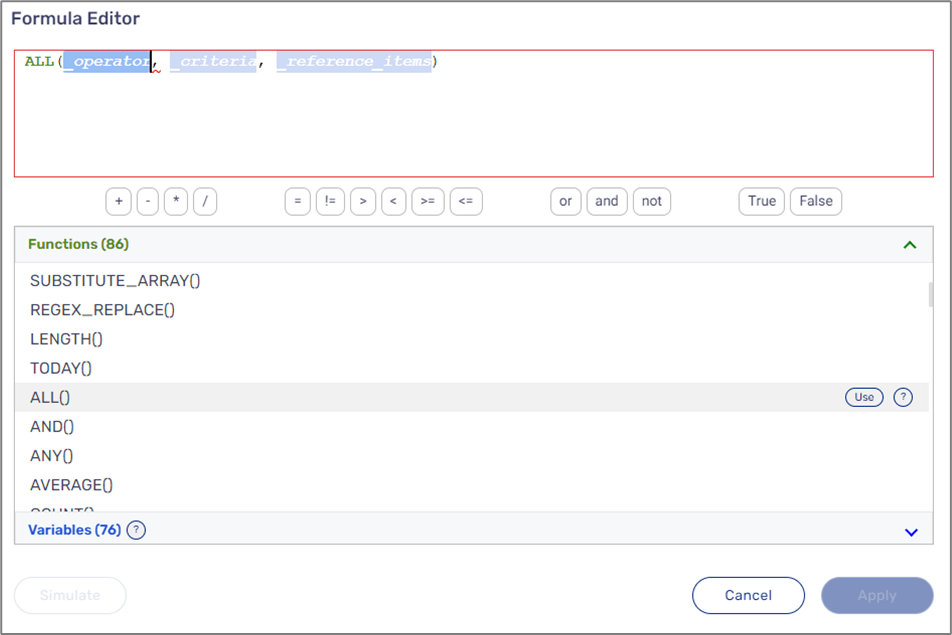
Figure 19: Added ALL() Function
The function will be configured according to Table 90:
Table 90: ALL() Function Parameters and Values
| Parameter | Value |
| _operator | "<" |
| _criteria | $num4 |
| _reference_item | NIM ($num1,$num2,$num3) |
The function will look like this (see Figure 20):
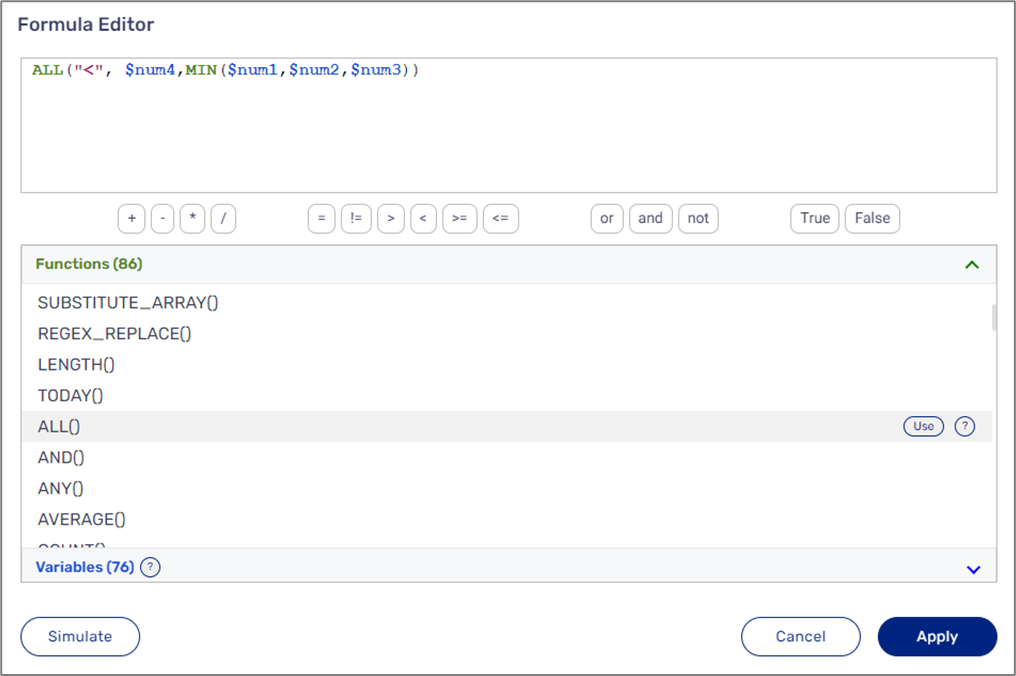
Figure 20: Configured Function
According to the configuration of the function, the result variable will contain True if the returned value from the MIN() function is smaller than the value of the num4 variable, else, False.
Returning an Array
We want to display customer information according to a specific ID.
Figure 21 describes a data structure that contains an object with nested variables (1):
- personalDetails (object)
- firstName (string)
- lastName (string)
- age (string)
- birthDate (string)
- idNumber (string)
The data structure also contains a string type variable named result_array (2) that will contain a returned Array and a string type variable, idNumber (3), that will be used to determine the Array values that will be returned.

Figure 21: Data Structure
To use the formula editor, perform the following steps (see Figure 22 to Figure 25):
Figure 22: Formula Option
- Click the resultArray variable (1).
- Click the Value dropdown (2).
- Click Formula (3).
Result:
The Edit Formula button (4) appears:
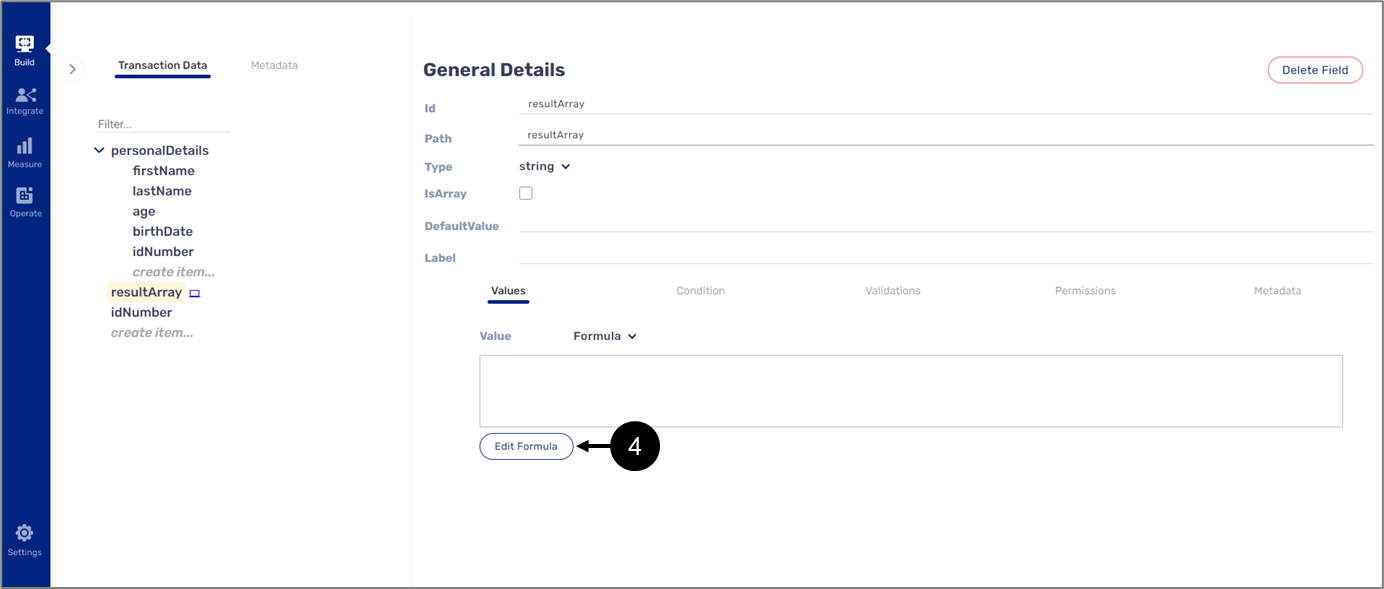
Figure 23: Edit Formula
- Click the Edit Formula button (4).
Result:
The Formula Editor window appears:
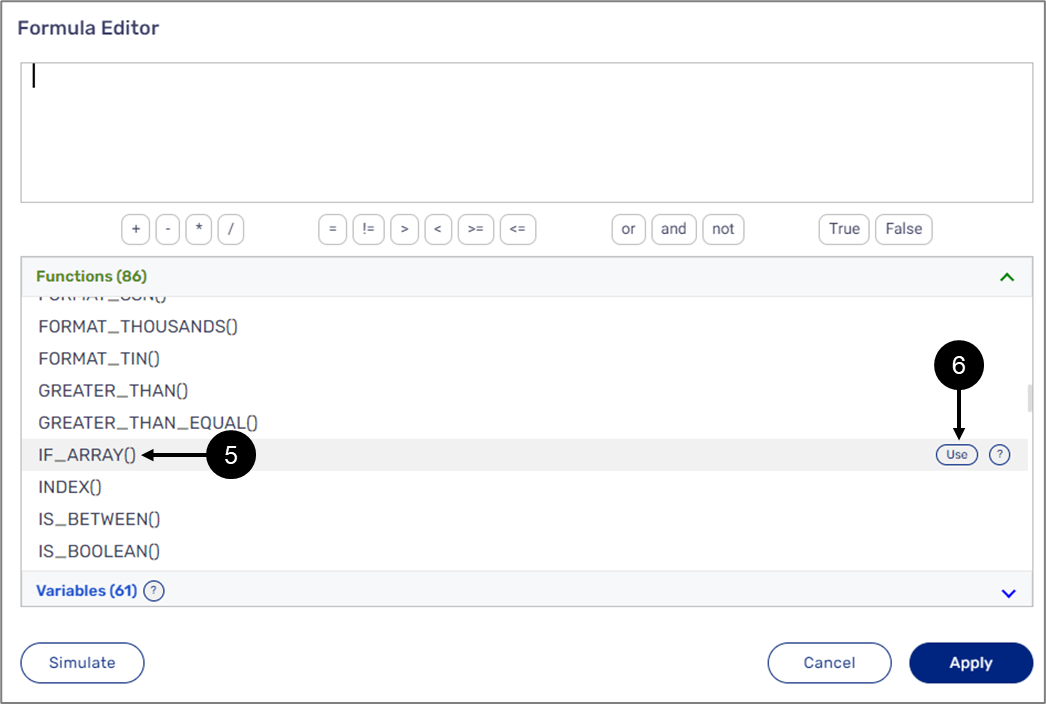
Figure 24: Adding the IF_ARRAY() Function
- Locate the IF_ARRAY() function (5).
- Double click it or click the Use button (6).
Result:
The function is added:
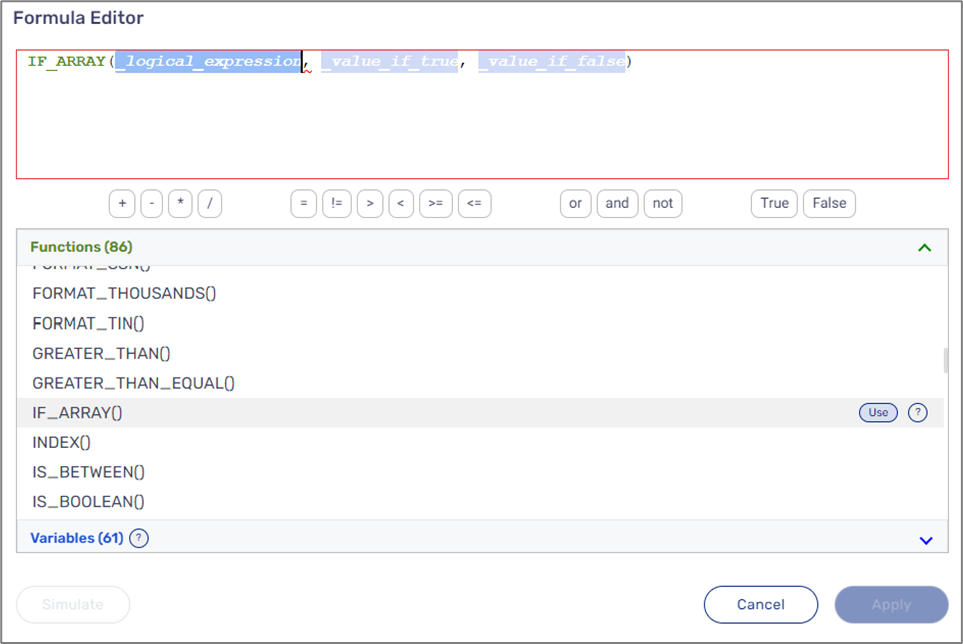
Figure 25: Added IF_ARRAY() Function
The function will be configured according to Table 91:
Table 91: IF_ARRAY() Function Parameters and Values
| Parameter | Value |
| _logical_expression | $personalDetails[0].idNumber = $idNumber |
| _value_if_true | TO_ARRAY($personalDetails[0].firstName, $personalDetails[0].lastName, $personalDetails[0].age, $personalDetails[0].birthDate, $personalDetails[0].idNumber |
The function will look like this (see Figure 26):
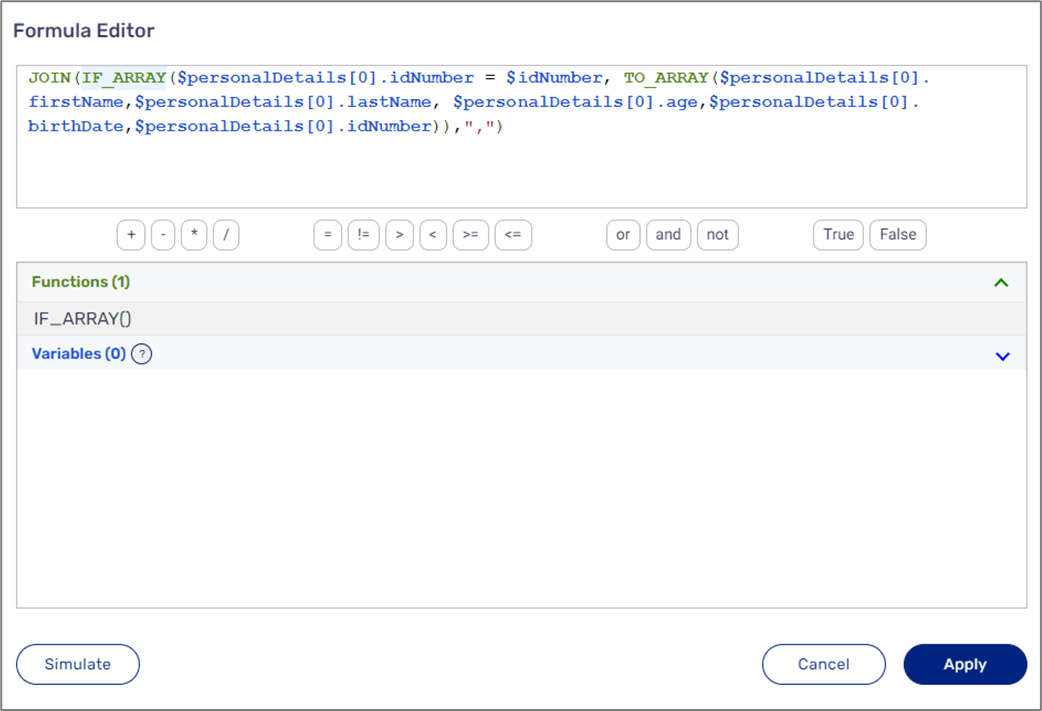
Figure 26: Configured Function
According to the configuration of the function, the resultArray variable will contain the values returned from the TO_ARRAY() function if the value of the idNumber variable equals the value of the personalDetails[0].idNumber item. The JOIN() function enables displaying multiple strings with a comma separating between values.
Using a Formula for conditioning
We want to display spouse information components only if the status of the end-user is Married.
Figure 27 describes a data structure that contains the following variables (1):
- isMarried (boolean)
- spouseDetails (object)
- fullName (string)
- birthDate (string)
- idNumber (string)
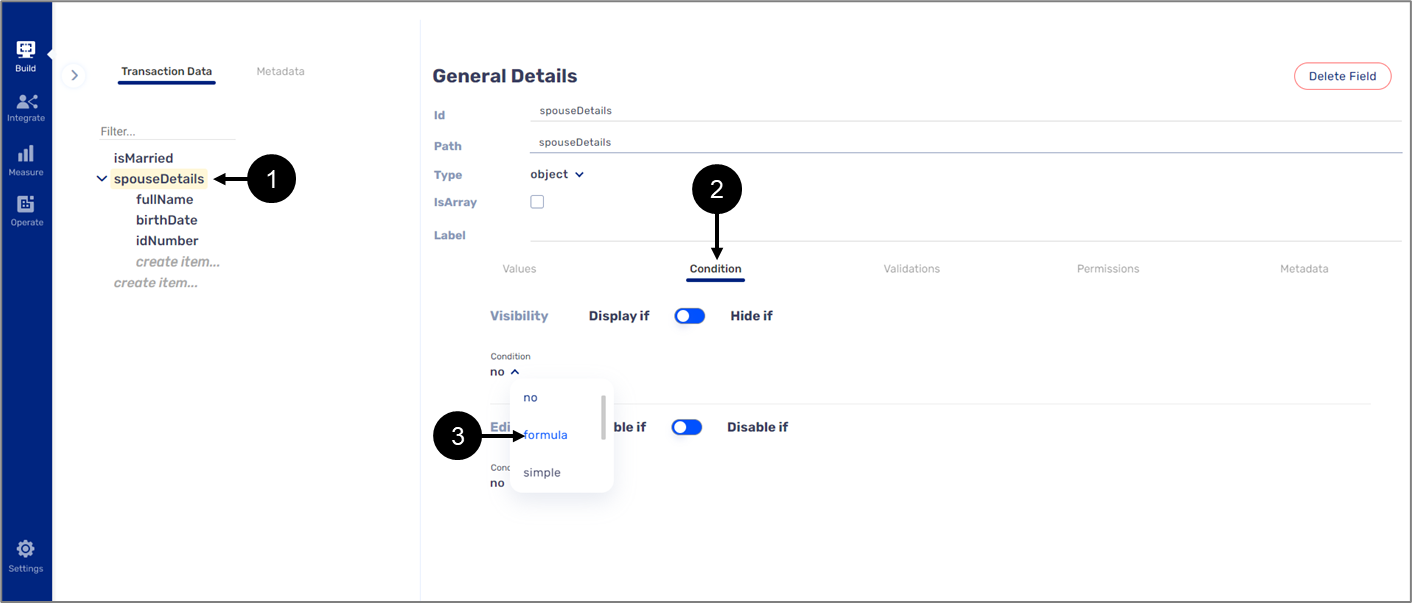
Figure 27: Data Structure
To use the Formula editor, perform the following steps (see Figure 28 to Figure 31):
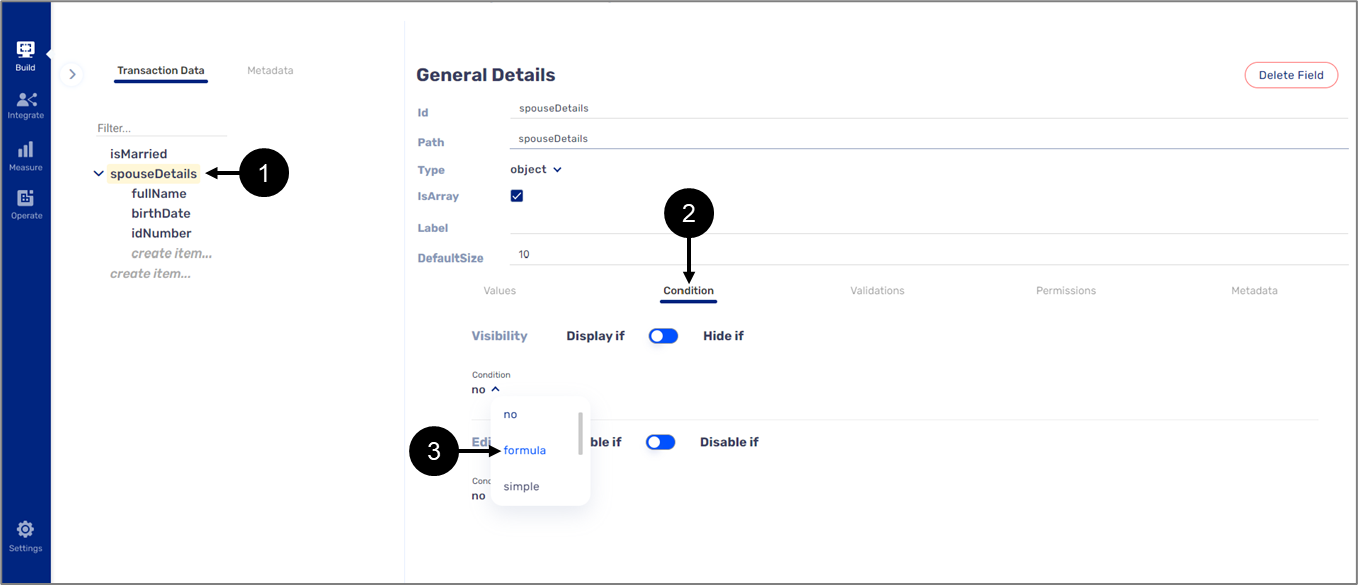
Figure 28: Formula Option
- Click the spouseDetails variable (1).
- Click Condition (2).
- Click the dropdown and select Formula (3).
Result:
The Edit Formula button (4) appears:
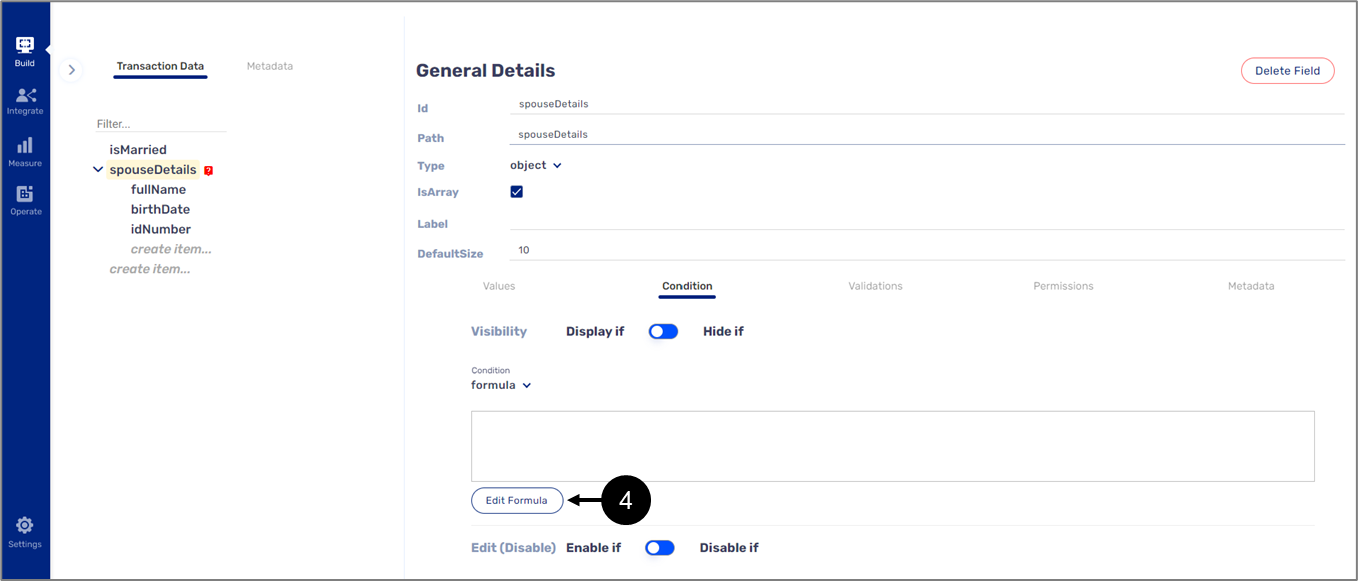
Figure 29: Edit Formula
- Click the Edit Formula button (4).
Result:
The Formula Editor window appears:
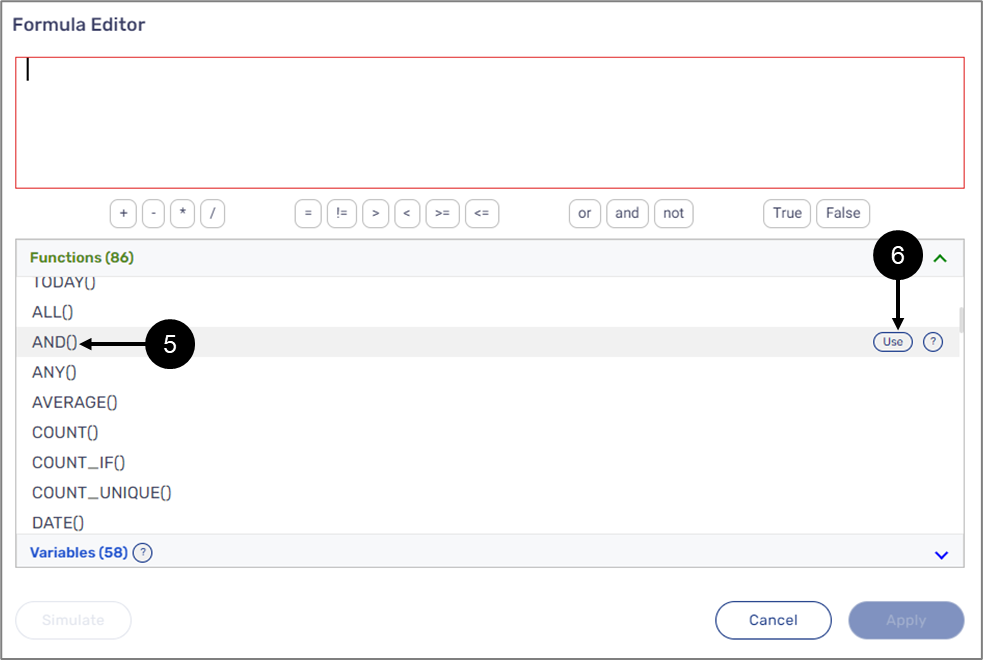
Figure 30: Adding the AND() Function
- Locate the AND() function (5).
- Double click it or click the Use button (6).
Result:
The function is added:
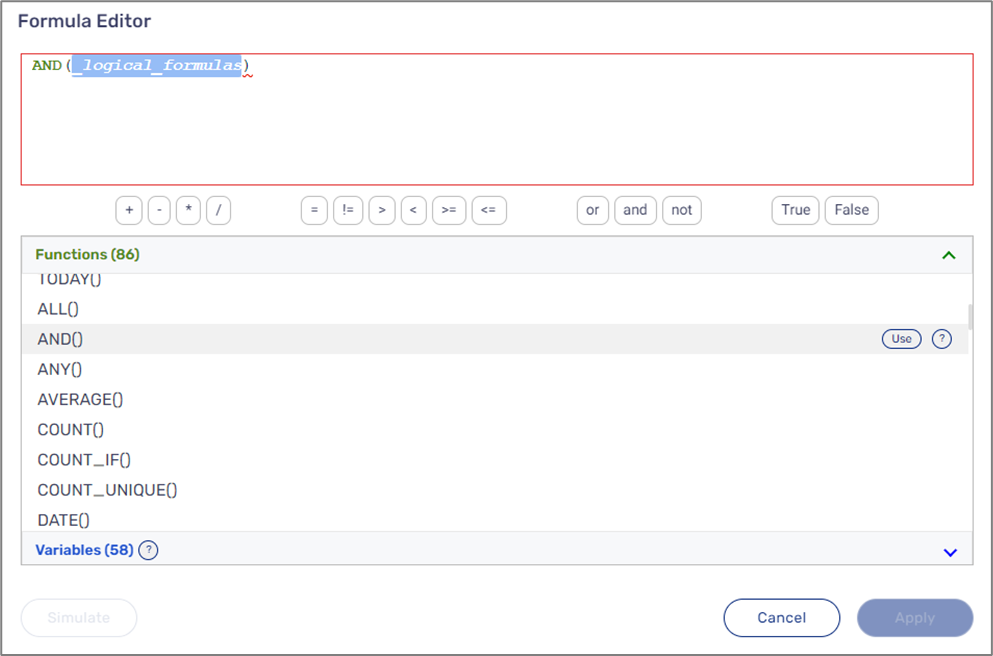
Figure 31: Added AND() Function
The function will be configured according to Table 92:
Table 92: AND() Function Parameter and Value
| Parameter | Value |
| _reference_item | $isMarried |
The function will look like this (see Figure 32):
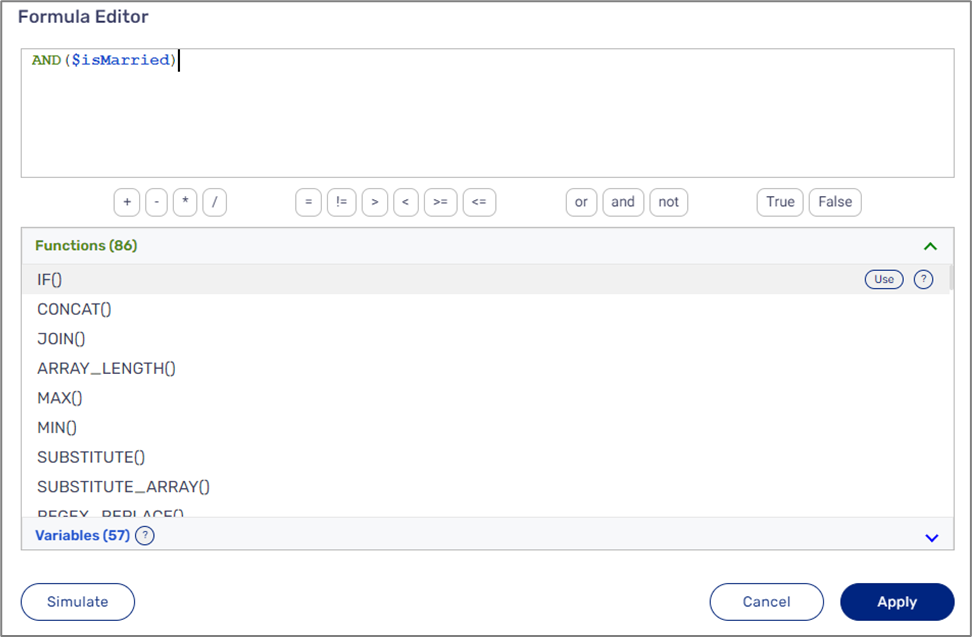
Figure 32: Configured Function
The function will return a True value if the isMarried variable contains a True value as well, else False. Because the formula was created using the Visibility condition dropdown, the appearance of the components connected to data items that are nested under the spouseDetails data item while using the digital process depends on the returned value of the AND() function:
- True - visible
- False - not visible
Formula Editor Simulator
(See Figure 33)
The simulator helps platform users tune up functions’ performance and optimize the Formula editor usage. Once a function is added and configured (1), the simulator can be accessed by clicking the Simulate button (2).
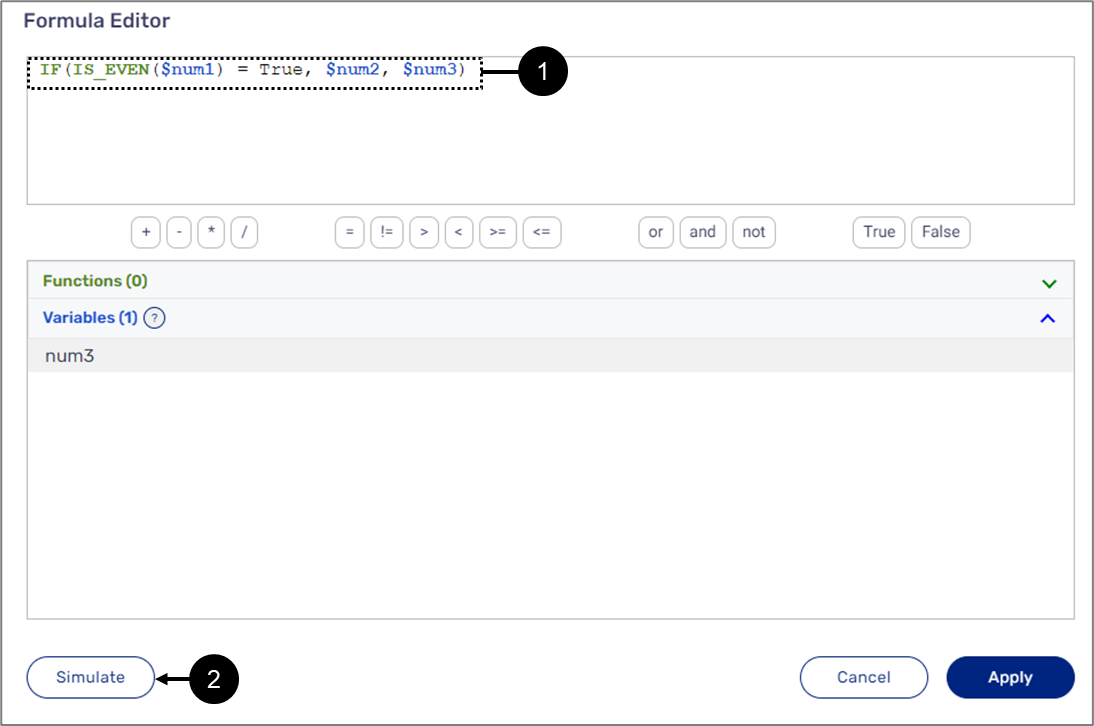
Figure 33: Accessing the Simulator
Use Case Example
(See Figure 34)
Figure 34 displays an IF() function that checks if the value of the num1 variable is even by comparing the IS_EVEN() function result to the boolean value True: 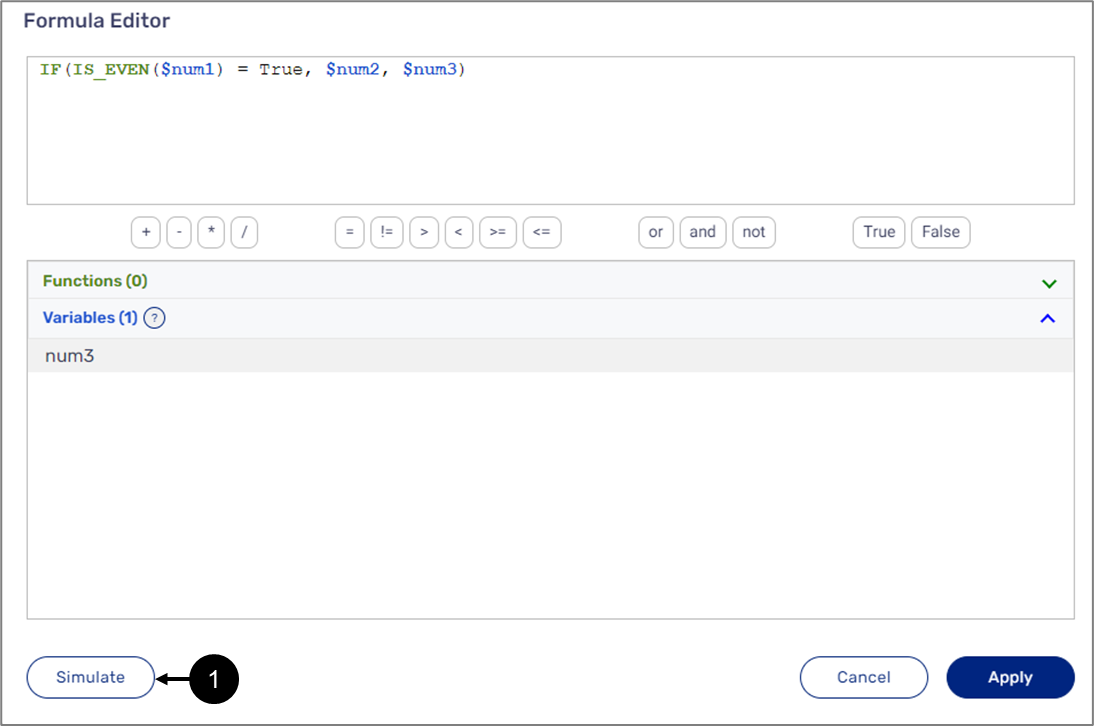
Figure 34: IF() Function
To check if the function works correctly using the simulator, perform the following steps:
- Click Simulate (1).
Result:
The Input (2) section appears:
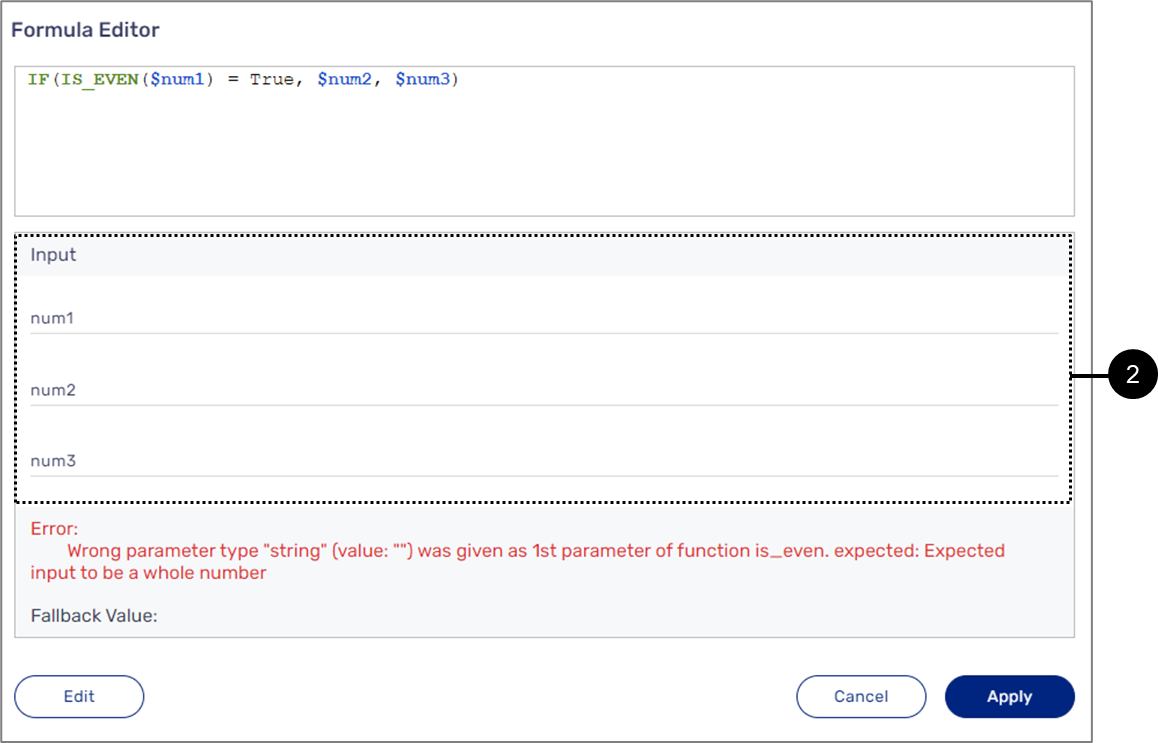
Figure 35: Input Values
- Input values according to the parameters (2).
Result:
A Result (3) appears:
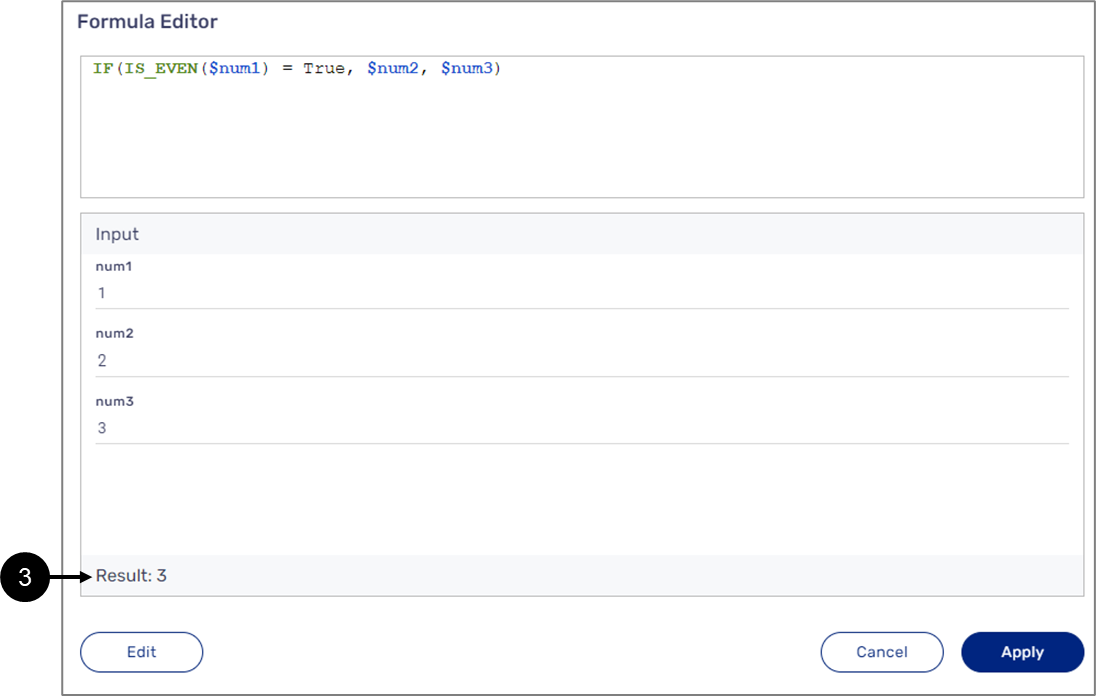
Figure 36: Simulated Result
- View the simulated results (3).
- Repeat steps 2 and 3 as needed to simulate additional input scenarios and results.
Appendix A - Formula Behaviors
The following appendix describes different formula behaviors.
Math Operators
See Table 93:
Table 93: Math Operators Behaviors
| Operator | Null (Null + 5) | Empty String (5 +"") | String (5 +"ab") |
| + | Converts null to 0 | Converts empty string to 0 | Error |
| _ | Converts null to 0 | Converts empty string to 0 | Error |
| * | Converts null to 0 | Converts empty string to 0 | Error |
| / | Converts null to 0 | Converts empty string to 0 | Error |
Comparison Operators
See Table 94 and Table 95:
Table 94: Comparison of Operators Behaviors
| Operator | Number Compare | String/Boolean compare | Dates Compare | String to Number | Numeric String to Number |
| = | Compares | Compares | Compares | False | Compares |
| != | Compares | Compares | Compares | True | Compares |
| < | Compares | Error | Compares | Error | Compares |
| > | Compares | Error | Compares | Error | Compares |
| >= | Compares | Error | Compares | Error | Compares |
| <= | Compares | Error | Compares | Error | Compares |
Table 95: Comparison of Operators Behaviors
| Operator | 0 to "" | "0" to "" | 0 to "0" | 0 to False | "" to False | Null to Something/Null/Unmatched Types Compare |
| = | False | False | True | False | False | False |
| != | True | True | False | True | True | True |
| < | Error | Error | False | Error | Error | Error |
| > | Error | Error | False | Error | Error | Error |
| >= | Error | Error | True | Error | Error | Error |
| <= | Error | Error | True | Error | Error | Error |
Logical Operators
See Table 96:
Table 96: Logical Operators
| Operator | Null |
| and | Converts null to false |
| or | Converts null to false |
| not | Converts null to false |
Date Functions
The following sections describe date functions behaviors.
DATE_ADD() Function
See Table 97:
Table 97: DATE_ADD() Function
| Null Date | Null_number_to_add | Null Units | String Some | Illegal Units |
| Error | Error | Error | Error | Error |
DATE_DIFF() Function
See Table 98:
Table 98: DATE_DIFF() Function
| Null Date | Null Units | Illegal Units |
| Error | Error | Error |
DATE() Function
See Table 99:
Table 99: DATE() Function
| Year/Month/Day Null | Wrong Year/Month/Day Number | Year/Month/Day Empty String |
| Error | Returns date | Error |
Other DATE Functions
See Table 100:
Table 100: Other Date Functions
| Function | Date Null | Date Invalid |
| Day() | Error | Error |
| Month() | Error | Error |
| Year() | Error | Error |
| WEEK_DAY() | Error | Error |
| WEEK_NUM() | Error | Error |
Math Functions
The following sections describe math functions behaviors.
COUNT(), COUNT_UNIQUE(), SUM(), AVERAGE(), MIN(), MAX() Functions
See Table 101:
Table 101: COUNT(), COUNT_UNIQUE,SUM(), AVERAGE(), MIN(), MAX() Functions
| Function | Null | Empty Array | Null/Empty String in Array | String in Array |
| COUNT() | Returns 0 | Returns 0 | Counts | Counts |
| COUNT_UNIQUE() | Returns 0 | Returns 0 | Counts | Counts |
| SUM() | Returns 0 | Returns 0 | Ignores it in calculation | Error |
| AVERAGE() | Null | Null | Ignores it in calculation | Error |
| MIN() | Null | Null | Ignores it in calculation | Error |
| MAX() | Null | Null | Ignores it in calculation | Error |
SUBTRACT(), DIVIDE(), MULTIPLY() Functions
See Table 102:
Table 102: SUBTRACT(), DIVIDE(), MULTIPLY() Functions
| Function | Null Value | Empty String Value | String Value |
| SUBTRACT() | Converts null to 0 | Converts empty string to 0 | Error |
| DIVIDE() | Converts null to 0 | Converts empty string to 0 | Error |
| MULTIPLY() | Converts null to 0 | Converts empty string to 0 | Error |
IS_EVEN(), IS_ODD Functions
See Table 103:
Table 103: IS_EVEN(), IS_ODD Functions
| Function | Null | 0 | Fraction | String | Empty String |
| IS_EVEN() | Error | True | Error | Error | Error |
| IS_ODD() | Error | False | Error | Error | Error |
SQURT() Function
See Table 104:
Table 104: SQURT() Function
| Null | String | Empty String | Negative |
| Error | True | Returns 0 | Error |
COUNT_IF(), SUM_IF() Functions
See Table 105:
Table 105: COUNT_IF(), SUM_IF() Functions
| Function | Null/Empty Array/Value Null | Null in Array | Empty String in Array | String in Array | Value Empty String |
| COUNT_IF() | Returns 0 | Ignores | If value number - ignores, else, compares | Compares | Compares |
| SUM_IF() | Returns 0 | Ignores | Ignores | Error | Compares |
IS_BETWEEN() Function
See Table 106:
Table 106: IS_BETWEEN() Function
| Checked Null | Checked Empty String | Checked String | val 1/2 Null, Empty String, or String | Is_val 1/2_Inclusive Null or Empty String |
| Error | Error | Error | Error | False |
POWER() Function
See Table 107:
Table 107: POWER() Function
| Base Null/Base Empty String | Base/Exponent String | Exponent Null/Empty String |
| Return 0 | Error | Returns 1 |
ROUND() Function
See Table 108:
Table 108: ROUND() Function
| Value Null | Value Empty String | Place Null/Negative/Empty String |
| Error | Error | Changes Place to 0 |
Information Functions
The following sections describe information functions behaviors.
IS_EMPTY() Function
See Table 109:
Table 109: IS_EMPTY() Function
| Null | Empty String |
| True | True |
IS_NUMBER() Function
See Table 110:
Table 110: IS_NUMBER() Function
| Null | Empty String | Infinity |
| False | False | True |
IS_EMPTY_ARRAY() Function
See Table 111:
Table 111: IS_EMPTY_ARRAY() Function
| Null | Empty String | Null in Array[Null] | Empty String in Array[""] |
| True | True | False | False |
IS_BOOLEAN(), IS_TEXT(), TYPE() Functions
See Table 112:
Table 112: IS_BOOLEAN(), IS_TEXT(), TYPE() Functions
| Function | Null | Empty String |
| IS_BOOLEAN() | False | False |
| IS_TEXT() | False | True |
| TYPE() | Returns 'null' | Returns 'string' |
Textual Functions
The following sections describe textual functions behaviors.
JOIN(), CONCAT() Functions
See Table 113:
Table 113: JOIN(), CONCAT() Functions
| Function | Null/Empty Array | Null in Array | Empty String - in Array/as Item |
| JOIN() | Return empty string | Converts null to empty string and joins | Joins |
| CONCAT() | Return empty string | Converts null to empty string and concats | Contacts |
LENGTH(), LOWER(), UPPER(), PROPER() Functions
See Table 114:
Table 114: LENGTH(), LOWER(), UPPER(), PROPER() Functions
| Function | Null/Empty String |
| LENGTH() | Returns 0 |
| LOWER() | Returns empty string |
| UPPER() | Returns empty string |
| PROPER() | Returns empty string |
PAD() Function
See Table 115:
Table 115: PAD() Function
| Null | Empty String | Length <=0 | Illegal Format (no 0/1) |
| Pads as empty string | Pads | Error | Error |
POSITION() Function
See Table 116:
Table 116: POSITION() Function
| Str Null/Empty/Not Found/Search Null/Search Empty | Negative Start_From |
| -1 | Starts from 0 |
REPLACE() Function
See Table 117:
Table 117: REPLACE() Function
| Str Null/Empty | Length < 0 | Position >= Str Length | Replacement Null | Position < 1 |
| Returns empty string | Error | Returns original string | Replaces with empty string | Error |
SUBSTITUTE() Function
See Table 118:
Table 118: SUBSTITUTE() Function
| Str Null/Empty | Occurrences < 0 /Search Null/Empty | Replace_With_Null/Empty |
| Returns empty string | Returns original string | Replaces with empty string |
SUBSTRING() Function
See Table 119:
Table 119: SUBSTRING() Function
| Str Null/Empty/Length = 0/ Negative Length/ Start > Str Length | Start < 1 |
| Returns empty string | Starts from 1 |
TRIM() Function
See Table 120:
Table 120: TRIM() Function
| Str Null/Empty | Pad Null/Empty |
| Returns empty string | Returns original string |
SPLIT() Function
See Table 121:
Table 121: SPLIT() Function
| Str Null/Empty | Split by Null/Empty |
| Returns [] | Returns the original string in Array |
REGEX_EXTRACT, REGEX_MATCH() Functions
See Table 122:
Table 122: REGEX_EXTRACT(), REGEX_MATCH() Functions
| Function | Text Null/Empty/REGEX Null/Empty/Not Found |
| REGEX_EXTRACT() | Returns empty string |
| REGEX_MATHC() | Returns false |
REGEX_REPLACE() Function
See Table 123:
Table 123: REGEX_REPLACE() Function
| Text Null/Empty | REGEX Null/Empty | Replace with Null/Empty |
| Returns empty string | Returns original string | Replaces with an empty string |
Array Functions
The following sections describe array functions behaviors.
LOOKUP(), LOOKUP_ARRAY() Functions
See Table 124:
Table 124: LOOKUP(), LOOKUP_ARRAY() Functions
| Function | Not Found/Search is Null/Lookup_Array is Null/Empty/Result_Array is Null/Empty | Result Index not in Result_Array |
| LOOKUP() | Returns null | Returns null |
| LOOKUP_ARRAY() | Returns [] | Returns only found items |
ARRAY_LENGTH() Function
See Table 125:
Table 125: ARRAY_LENGTH() Function
| Array is Null/Empty |
| Returns 0 |
LOWER_ARRAY, UPPER_ARRAY(), REMOVE_EMPTY(), UNIQUE() Functions
See Table 126:
Table 126: LOWER_ARRAY(), UPPER_ARRAY(), REMOVE_EMPTY(), UNIQUE() Functions
| Function | Array is Null/Empty | Array Contains Null/Empty String |
| LOWER_ARRAY() | Returns [] | Returns empty string |
| UPPER_ARRAY() | Returns [] | Returns empty string |
| REMOVE_EMPTY() | Removes it | Removes it |
| UNIQUE() | Returns [] | Keeps it |
FILTER() Function
See Table 127:
Table 127: FILTER() Function
| Not Found/Search is Null/Array is Null/Empty |
| Returns [] |
PAD_ARRAY() Function
See Table 128:
Table 128: PAD_ARRY() Function
| Null/Empty Array | Array Contains Null | Array Contains Empty String | Length <= 0/Illegal Format (no 0/1) |
| Returns [] | Pads as empty string | Pads | Error |
SUBSTITUTE_ARRAY() Function
See Table 129:
Table 129: SUBSTITUTE_ARRAY() Function
| Array Null/Empty | Occurrences < 0 /Search Null/Empty | Replace_With_Null/Empty |
| Returns [] | Returns original array | Replaces with an empty string |
VALUE() Function
See Table 130:
Table 130: VALUE() Function
| Array Null/Empty/Index Null/Index Empty String/Index Negative/Not Found |
| Returns null |
Conversion Functions
The following sections describe conversion functions behaviors.
TO_ARRAY() Function
See Table 131:
Table 131: TO_ARRAY() Function
| Null | Empty String |
| Adds null to array | Adds empty string to array |
TO_NUM() Function
See Table 132:
Table 132: TO_NUM() Function
| Null/Empty String/String/Date/number/Boolean | Numeric String |
| Error | Returns number |
TO_TEXT() Function
See Table 133:
Table 133: TO_TEXT() Function
| String/Numeric String/Number/Boolean | Null | Empty String | Date |
| Returns string | Returns null | Returns " | Error |
DATE_FORMAT() Function
See Table 134:
Table 134: DATE_FORMAT() Function
| Date Null/Format Null/Empty |
| Error |
FORMAT_TIN(), FORMAT_SSN, FORMAT_THOUSANDS() Functions
See Table 135:
Table 135: FORMAT_TIN(), FORMAT_SSN, FORMAT_THOUSANDS Functions
| Function | Null/Empty String | Array Contains Null | String | Numeric String |
| FORMAT_TIN() | Returns empty string | Pads as empty string | Format if length is 9, else returns as is | Format if length is 9, else returns as is |
| FORMAT_SSN() | Returns empty string | Returns empty string | Format if length is 9, else returns as is | Format if length is 9, else returns as is |
| FORMAT_THOUSANDS() | Returns empty string | Returns empty string | returns as is | Formats |
FORMAT_PRECISION() Function
See Table 136:
Table 136: FORMAT_PRECISION() Function
| String Null/Empty/Precision Null/Empty/Fraction/Negative |
| returns as is |
Logical Functions
The following sections describe conversion functions behaviors.
NOT() Function
See Table 137:
Table 137: NOT() Function
| Null |
| Returns true (null is false) |
AND(), OR() Functions
See Table 138:
Table 138: AND(), OR() Functions
| Function | Null/Empty Array | Null in Array |
| AND() | Returns false | Converts null to false |
| OR() | Returns false | Converts null to false |
ALL(), ANY() Functions
See Table 139:
Table 139: ALL(), ALL() Functions
| Function | Null Value/Array/Empty Array | Null in Array |
| ALL() | Returns false | Ignores it |
| ANY() | Returns false | Ignores it |
IF(), IF_ARRAY() Functions
See Table 140:
Table 140: IF(), IF_ARRAY() Functions
| Function | Null condition | Null Then/Else | No Else and False condition |
| IF() | Returns else | returns as is | returns error |
| IF_ARRAY() | Returns else | returns as is | returns error |
SWITCH(), SWITCH_ARRAY() Functions
See Table 141:
Table 141: SWITCH(), SWITCH_ARRAY() Functions
| Function | Checked Null | Case Null | Result/Default Null |
| SWITCH() | Returns default | Cannot be true | returns as is |
| SWITCH_ARRAY() | Returns default | Cannot be true | returns as is |